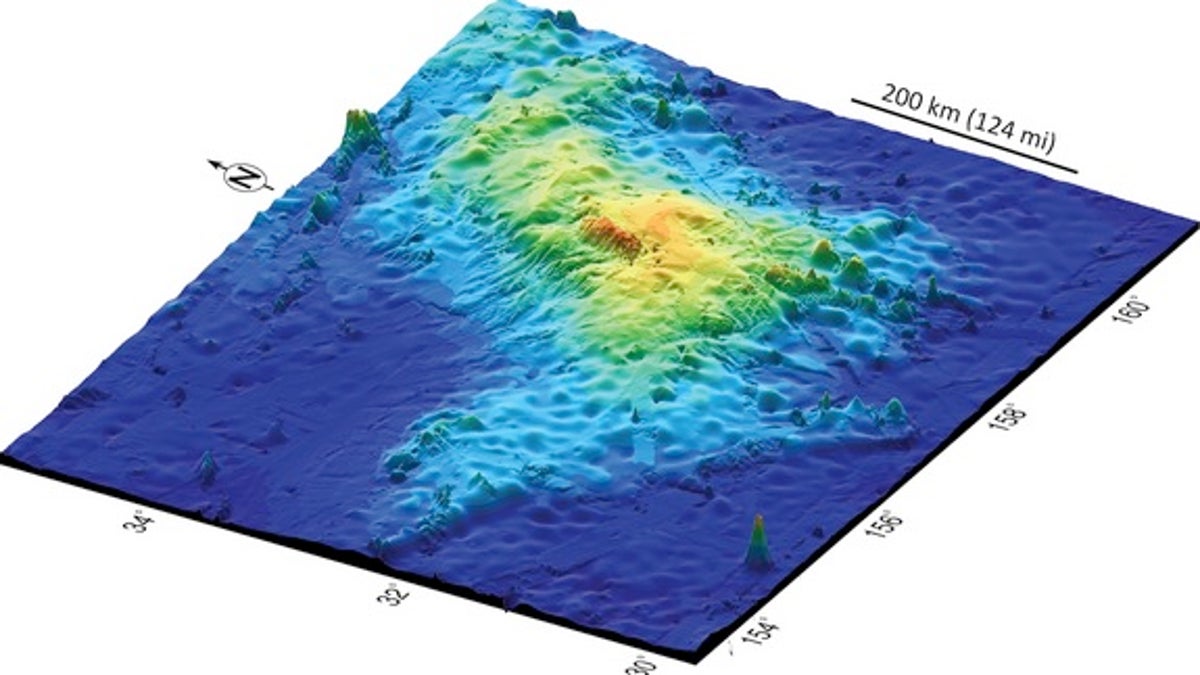
A 3D map of Tamu Massif, the world's biggest volcano. (William Sager)
The world's largest volcano lurks beneath the Pacific Ocean, researchers announced in the journal Nature Geoscience.
Called the Tamu Massif, the enormous mound dwarfs the previous record holder, Hawaii's Mauna Loa, and is only 25 percent smaller than Olympus Mons on Mars, the biggest volcano in Earth's solar system, said William Sager, lead study author and a geologist at the University of Houston.
"We think this is a class of volcano that hasn't been recognized before," Sager said. "The slopes are very shallow. If you were standing on this thing, you would have a difficult time telling which way was downhill."
[summary]
Tamu is 400 miles wide but only about 2.5 miles tall. It erupted for a few million years during the early Cretaceous period, about 144 million years ago, and has been extinct since then, the researchers report. [50 Amazing Volcano Facts]
- Nature’s Fury: When Volcanoes Erupt
- Phoenix ‘UFO’ revealed as NASA experiment
- NASA aiming for moon again, this time from Va., to probe thinnest of atmospheres, lunar dust
- Russian resigns command of International Space Station for ‘better job’
- NSA efforts to crack encryption ‘betrayed Internet,’ expert says
Explaining ocean plateaus
Like other massive volcanoes, Tamu Massif seems to have a central cone that spewed lava down its broad, gentle slopes. The evidence comes from seismic surveys and lava samples painstakingly collected over several years of surveys by research ships. The seismic waves show lava flows dipping away from the summit of the volcano. There appears to be a series of calderas at the summit, similar in shape to the elongated and merged craters atop Mauna Loa, Sager said.
Until now, geologists thought Tamu Massif was simply part of an oceanic plateau called Shatsky Rise in the northwest Pacific Ocean. Oceanic plateaus are massive piles of lava whose origins are still a matter of active scientific debate. Some researchers think plumes of magma from deep in the mantle punch through the crust, flooding the surface with lava. Others suggest pre-existing weaknesses in the crust, such as tectonic-plate boundaries, provide passageways for magma from the mantle, the layer beneath the crust. Shatsky Rise formed atop a triple junction, where three plates pulled apart.
Tamu Massif's new status as a single volcano could help constrain models of how oceanic plateaus form, Sager said. "For anyone who wants to explain oceanic plateaus, we have new constraints," he told LiveScience. "They have to be able to explain this volcano forming in one spot and deliver this kind of magma supply in a short time."
Sager said other, bigger volcanoes could be awaiting discovery at other oceanic plateaus, such as Ontong Java Plateau, located north of the Solomon Islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean. "Structures that are under the ocean are really hard to study," he said.
Floating volcano
Oceanic plateaus are the biggest piles of lava on Earth. The outpourings have been linked to mass extinctions and climate change. The volume of Tamu Massif alone is about 600,000 cubic miles. The entire volcano is bigger than the British Isles or New Mexico.
Despite Tamu's huge size, the ship surveys showed little evidence the volcano's top ever poked above the sea. The world's biggest volcano has been hidden because it sits on thin oceanic crust (or lithosphere), which can't support its weight. Its top is about 6,500 feet below the ocean surface today.
"In the case of Shatsky Rise, it formed on virtually zero thickness lithosphere, so it's in isostatic balance," Sager said. "It's basically floating all the time, so the bulk of Tamu Massif is down in the mantle. The Hawaiian volcanoes erupted onto thick lithosphere, so it's like they have a raft to hold on to. They get up on top and push it down. And with Olympus Mons, it's like it formed on a two-by-four."
Sager and his colleagues have studied Shatsky Rise for decades, seeking to solve the puzzle of oceanic plateaus. About 20 years ago, they named Tamu Massif after Texas A&M University, Sager's former employer, he said.
Copyright 2013 LiveScience, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.








































