While there is no chance that asteroid 2012 DA14 will hit Earth this Friday, the asteroid's flyby is history-making for several other reasons.
1. This is asteroid 2012 DA14's closest pass ever
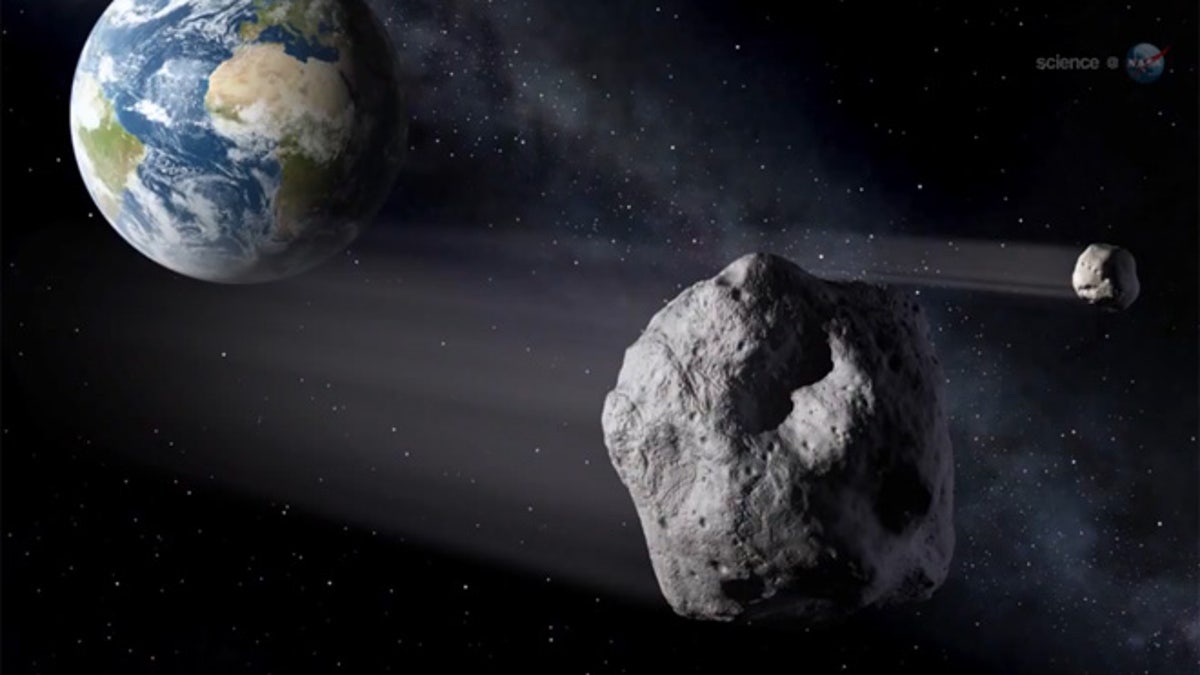

Talk about a close shave. Asteroid 2012DA14 will fly past Earth closer than many man-made satellites. (NASA)
Using intricate mapping techniques, researchers have already plotted the 150-foot space rock's trajectory far out into the future. When the asteroid flies by Earth, the planet's gravity will force the asteroid into a new orbit that won't bring it this close to the Earth for years to come. [Asteroid 2012 DA14's Close Shave Explained (Infographic)]
2. Asteroids like 2012 DA14 have hit Earth before
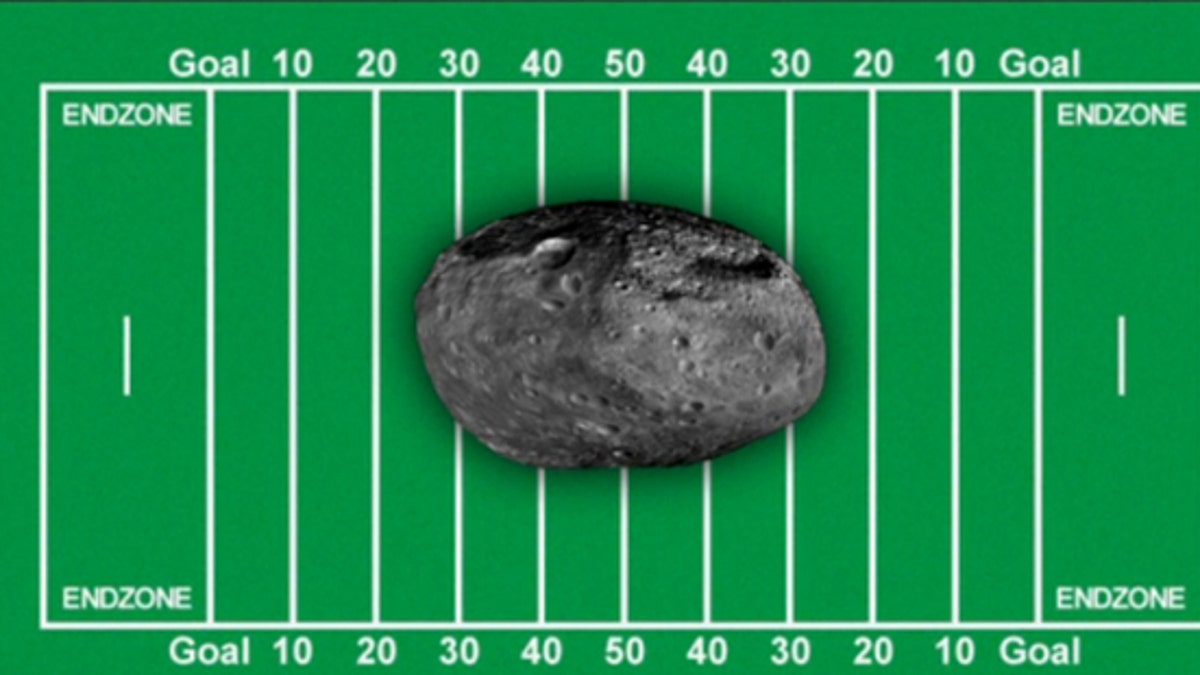

Asteroid 2012 DA14 is about the size of half a football field and will make a close approach to Earth on Feb. 15. (NASA)
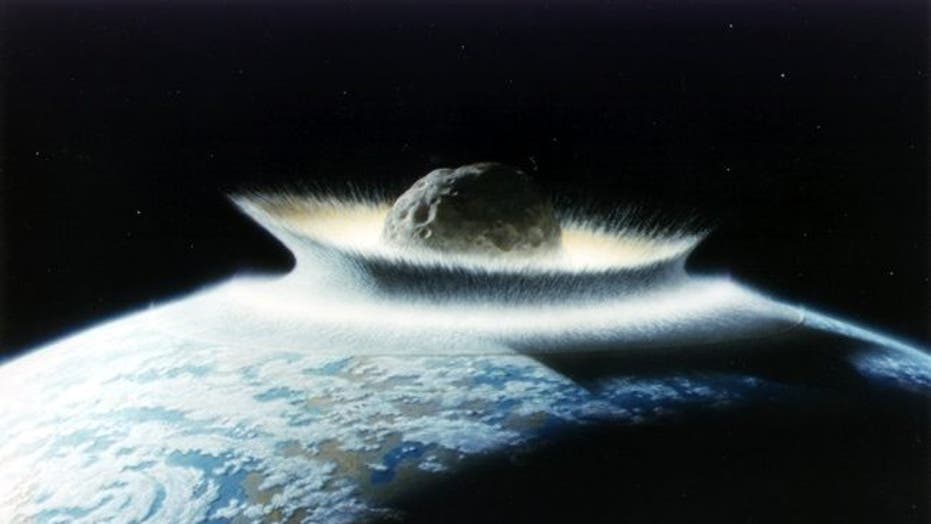
Scientists think the "Tunguska Event" over Siberia in 1908 was caused by a 100-foot asteroid. This space rock exploded in midair, leveling trees across 825 square miles in the region.
If 2012 DA14 did enter Earth's atmosphere, it probably would react similarly — exploding above the ground and causing destruction over a wide area, but not endangering human civilization or causing other major global problems.
3. 2012 DA14 was discovered by amateur astronomers

This NASA diagram depicting the passage of asteroid 2012 DA14 through the Earth-moon system on Feb. 15, 2013 (NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Asteroid 2012 DA14 was discovered by a team of amateur astronomers affiliated with the La Sagra Sky Survey at the Astronomical Observatory of Mallorca in southern Spain on Feb. 23, 2012.
At the time, the asteroid was about 2.7 million miles away from Earth. After the group reported the finding, NASA and other space agency scientists began tracking the asteroid to track its path and make sure it posed no threat to the planet.
4. Its closest approach point will be over Sumatra
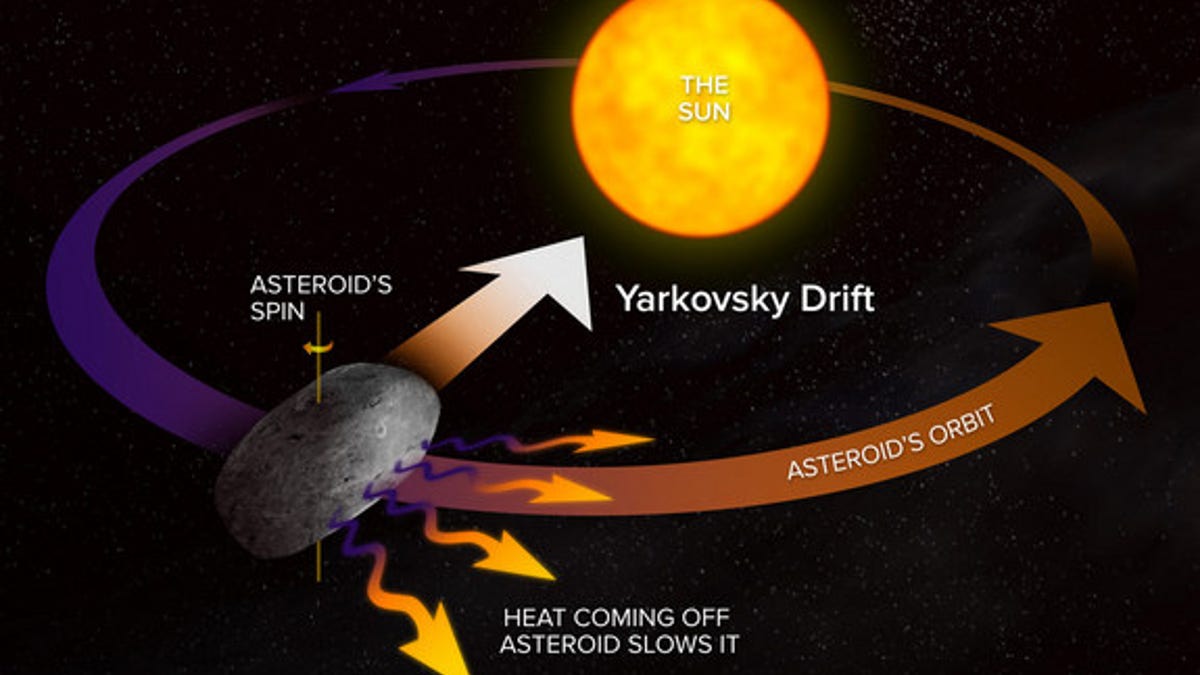
This diagram shows how the Yarkovsky Effect slows an asteroid's orbital motion; opposite rotation direction would speed up the orbital motion. Astronomers around the world are preparing to study the close approach of asteroid 2012 DA14 on Feb. (Alexandra Bolling, NRAO/AUI/NSF)
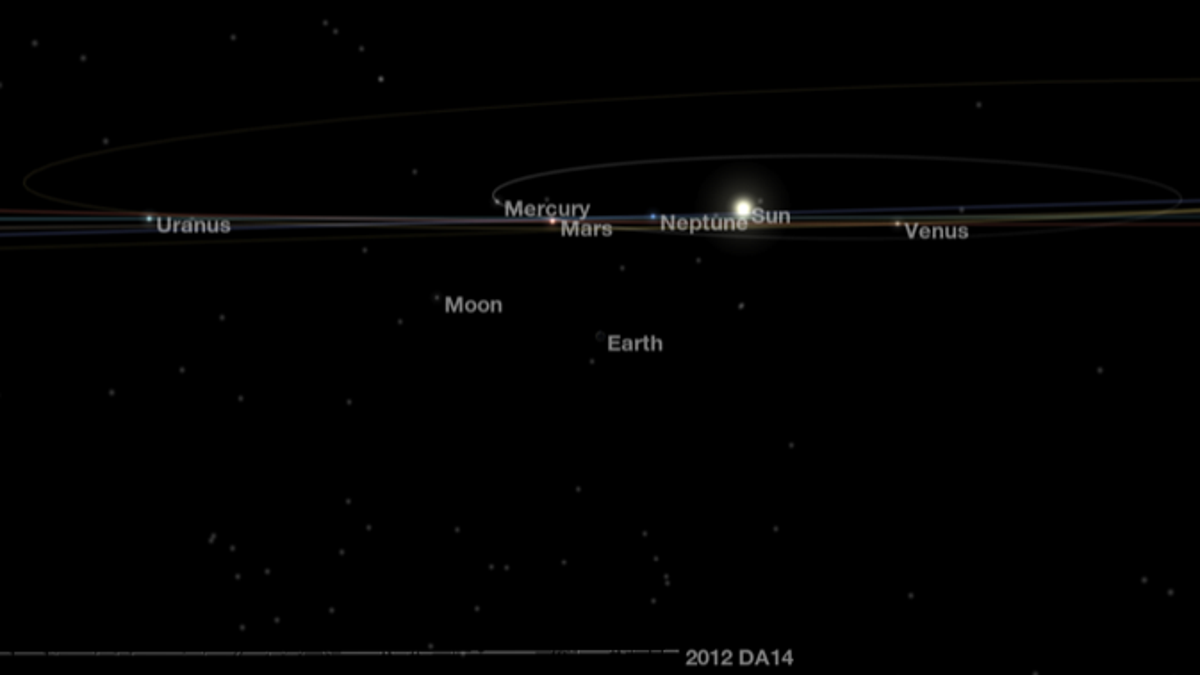
On Friday, when asteroid 2012 DA14 approaches within 17,200 miles of Earth, it will be over Sumatra, Indonesia at its closest point while zipping by the planet. That's just one-thirteenth the average distance from Earth to the moon.
At its closest approach on Friday at 2:24 p.m. EST (1924 GMT), the asteroid will be 5,000 miles closer to Earth than the ring of GPS, weather and communications satellites in orbit around the planet. Still, the satellites and the planet are safe from impact, researchers say.
5. Asteroids like 2012 DA14 fly by Earth every 40 years
Based on a statistical analysis, NASA researchers have found that asteroids like 2012 DA14 only graze Earth this closely once every 40 years or so. Similar asteroids can actually hit the Earth once every 1,200 years.
Larger asteroids are even less likely to give the planet such a close shave. NASA researchers say that their Near Earth Object Program has helped to detect and track 90 percent of the largest near-Earth asteroids, and so far none of these behemoths are known to pose an impact threat in the foreseeable future.
NASA will also be live-streaming the flyby via a telescope at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. from 6 p.m. to 9 p.m. ET (2100 to 0200 Feb. 16 GMT) on Friday.









































