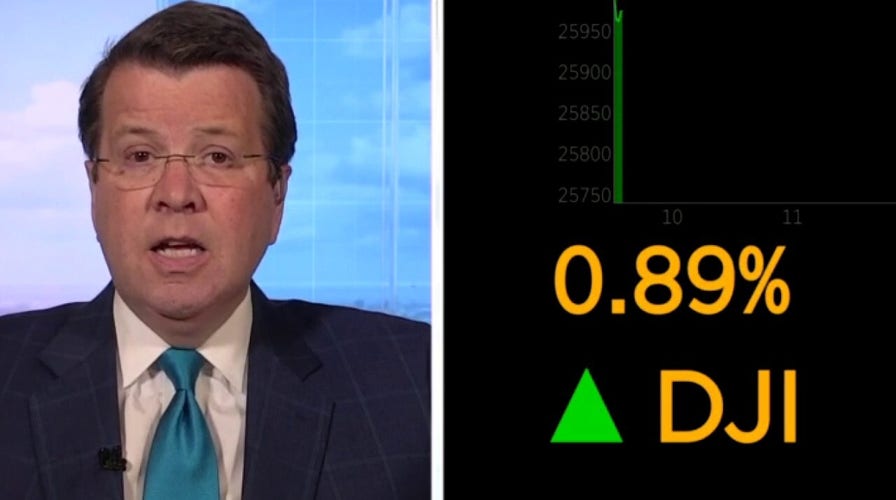
Neil Cavuto on 'highly feared' jobs report: 'Not as grim' as they thought
Neil Cavuto reacts to a new jobs report that came in well below expectations providing a boost to the stock market
The economy is mired in a recession, and any rebound in hiring will likely be painfully slow. Economists foresee unemployment remaining in double digits through the November elections and into 2021.
Oxford Economics, a consulting firm, estimates that the economy will regain 17 million jobs by year’s end, a huge increase by historic standards. But that would make up barely more than half the losses.
Seth Carpenter, an economist at UBS, said that after an initial bounce-back, future hiring will likely be slow and could be interrupted by another wave of the pandemic.
Adam Ozimek, chief economist at Upwork, notes that the fastest year for job growth since the Great Recession was 3 million jobs in 2014. Even at that pace, it would take at least several years to return to the pre-pandemic job market.
CLICK HERE FOR COMPLETE CORONAVIRUS COVERAGE
The damage to America’s job market from the viral outbreak will come into sharper focus Friday when the government releases the May employment report: Eight million more jobs are estimated to have been lost. Unemployment could near 20 percent. And potentially fewer than half of all adults may be working. Beneath the dismal figures will be signs that job cuts, severe as they are, are slowing as more businesses gradually or partially reopen.
Since mid-March, more than 40 million Americans have applied for unemployment benefits. That doesn’t mean that that many people are still unemployed. The figure likely includes some duplicate filings: In some states, self-employed and “gig” workers applied under their regular state unemployment systems before they were able to file under a new federal program that has made them eligible for benefits for the first time.
In addition, some people who lost jobs early and applied for unemployment aid have been rehired. That, along with slowing layoffs, helps explain why the net job loss for May is expected to be far less than April’s. Goldman Sachs estimates that up to 3 million people who were initially laid off have already been rehired.
Weekly surveys of small businesses by the Census Bureau show an uptick in the number of such companies hiring and providing more hours of work, though the gains are slight. In mid-May, the most recent data available, nearly 10 percent of small companies surveyed said they had added jobs in the past week, and 12 percent said they had added hours. Both figures were roughly double their level three weeks earlier.
Still, 16 percent said they had cut jobs, and a third said they were still cutting hours — figures that are consistent with ongoing but smaller job cuts in May.
Three-quarters of states have allowed dining-in services to resume at restaurants, though most are still restricting total capacity. Many states have reopened gyms, hair salons and movie theaters. But a meaningful rebound will require greater public willingness to return to their old activities without fear of contracting the virus.
CORONAVIRUS: WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Adam Kamins, senior regional economist at Moodys Analytics, said this probably won’t happen until a vaccine is available or testing expands significantly.
“It certainly doesn’t help to have this layer of uncertainty added on,” Kamins said.
Heidi Shierholz, senior economist at the progressive Economic Policy Institute and a former chief economist at the Labor Department, suggested that more government aid will be necessary to keep consumers and businesses afloat so that many laid-off workers will have jobs to return to.
“Those jobs are not going to come back if the federal government doesn’t do the things it needs to do to stimulate the economy, so that the demand and confidence is going to be there, so that those businesses will need to call workers back,” Shierholz said.
The Associated Press contributed to this report.