Move Back
ADVERTISEMENT
Skip- Published27 Images
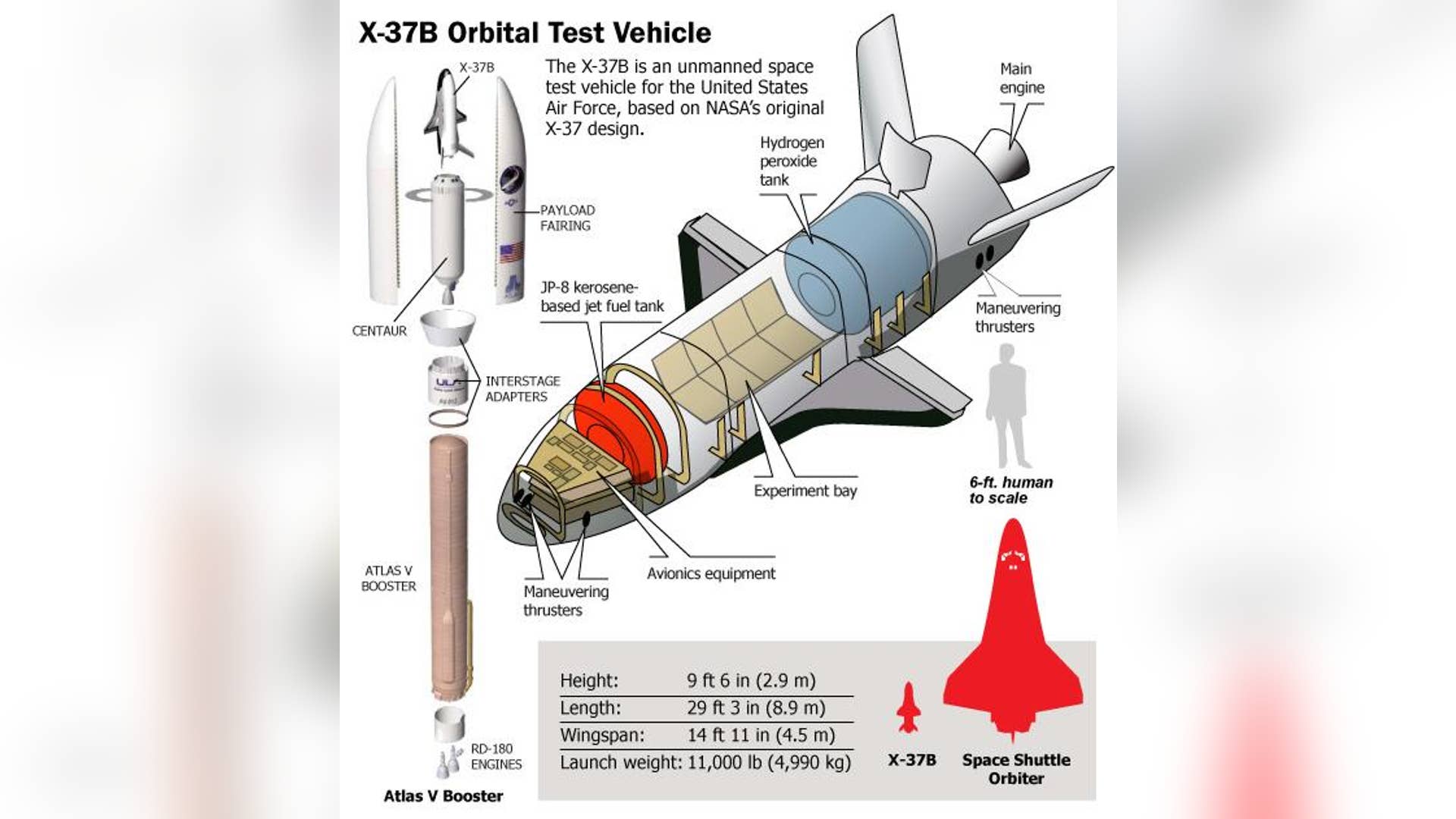
Inside the Air Force's secret space plane
The U.S. Air Force launched the robotic X-37B space plane in early 2010 on a space mission that remains a secret -- even after the craft touched ground 225 days later at Vandenberg Air Force Base. In early 2011, the ship took off again on its latest mission.
![minishuttle_2]()
![minishuttle_1]()
![NASA's X-37B Lands]()
![NASA's X-37B Lands]()
![NASA's X-37B Lands]()
![NASA's X-37B Lands]()
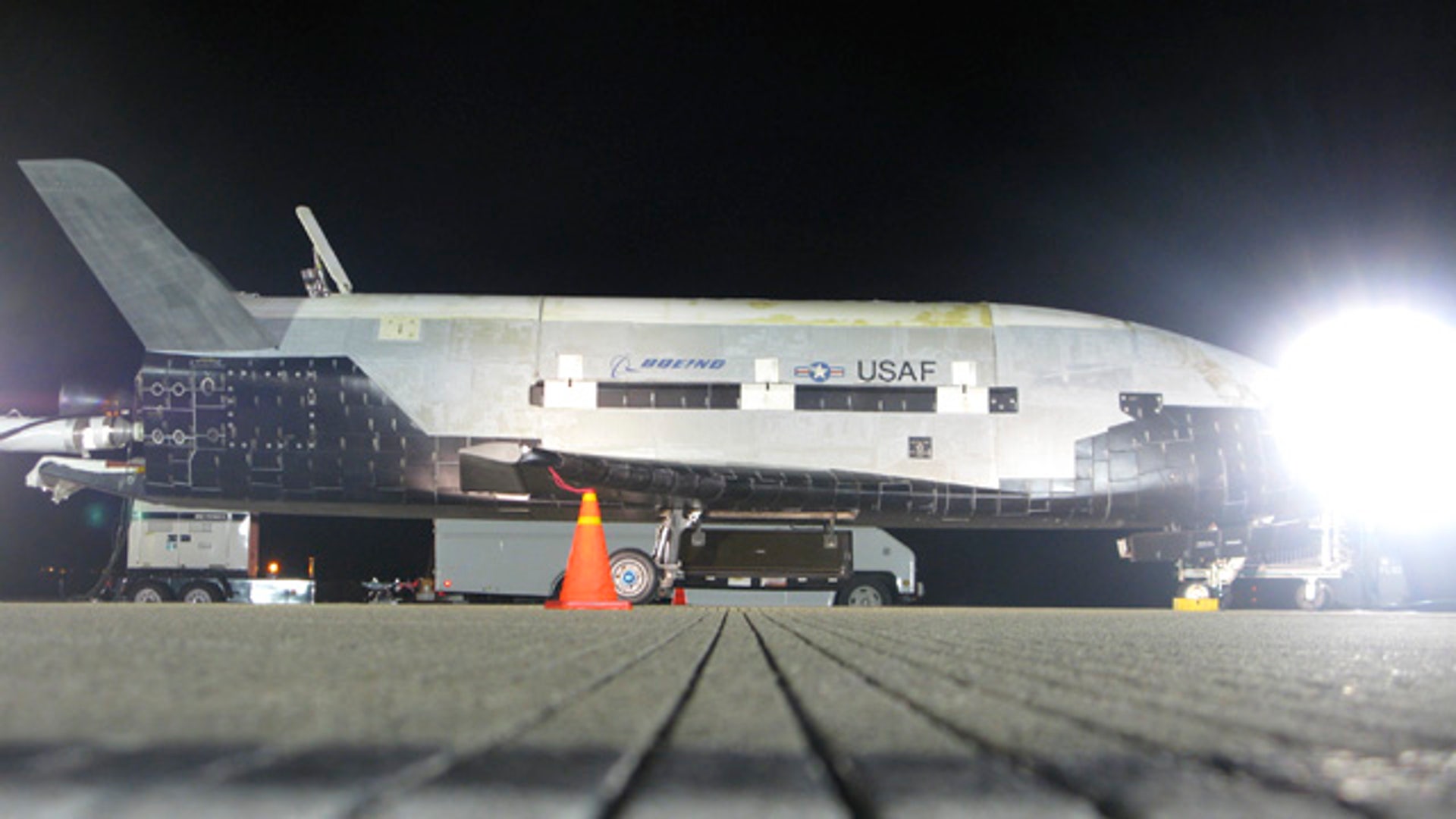
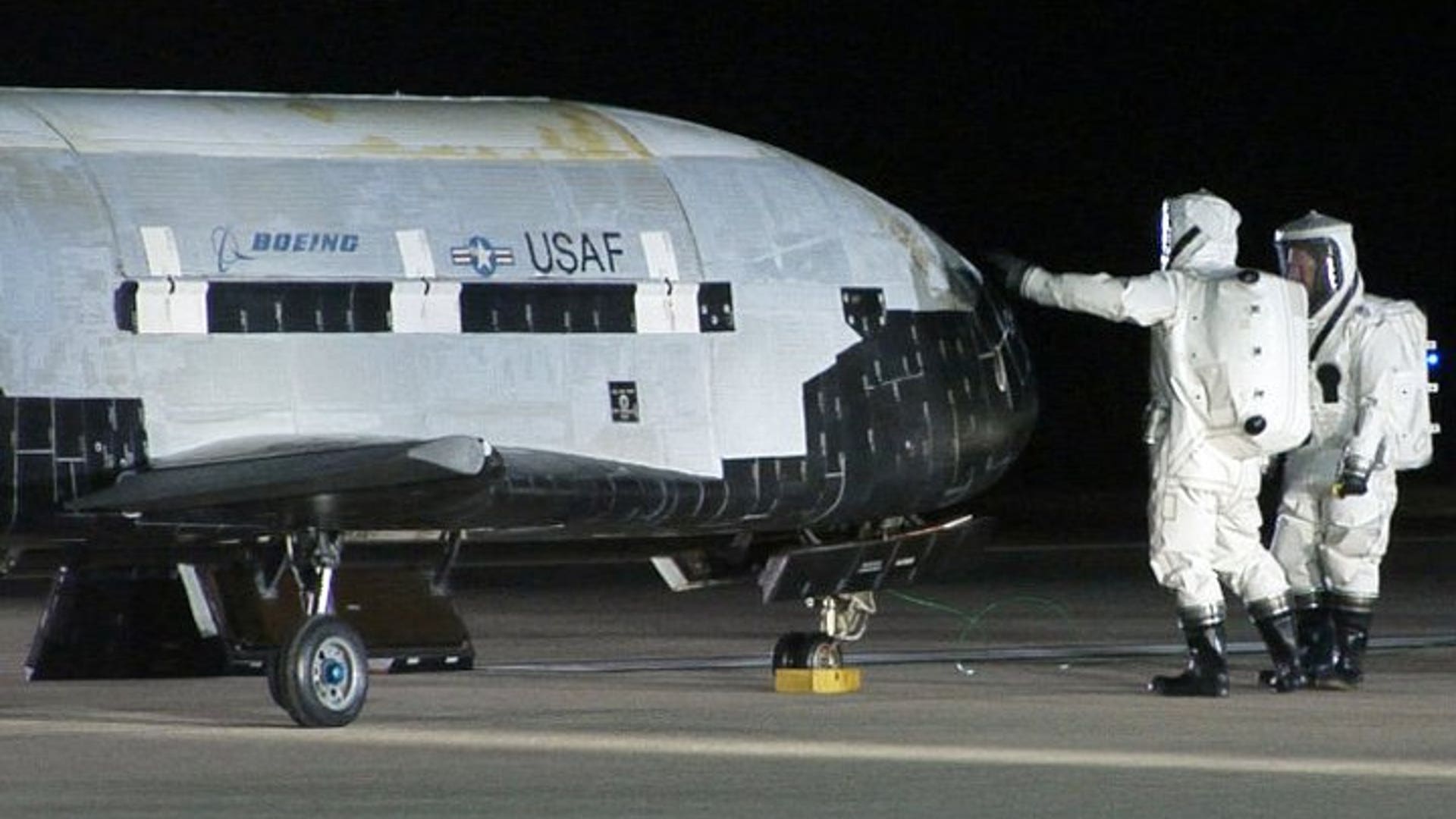
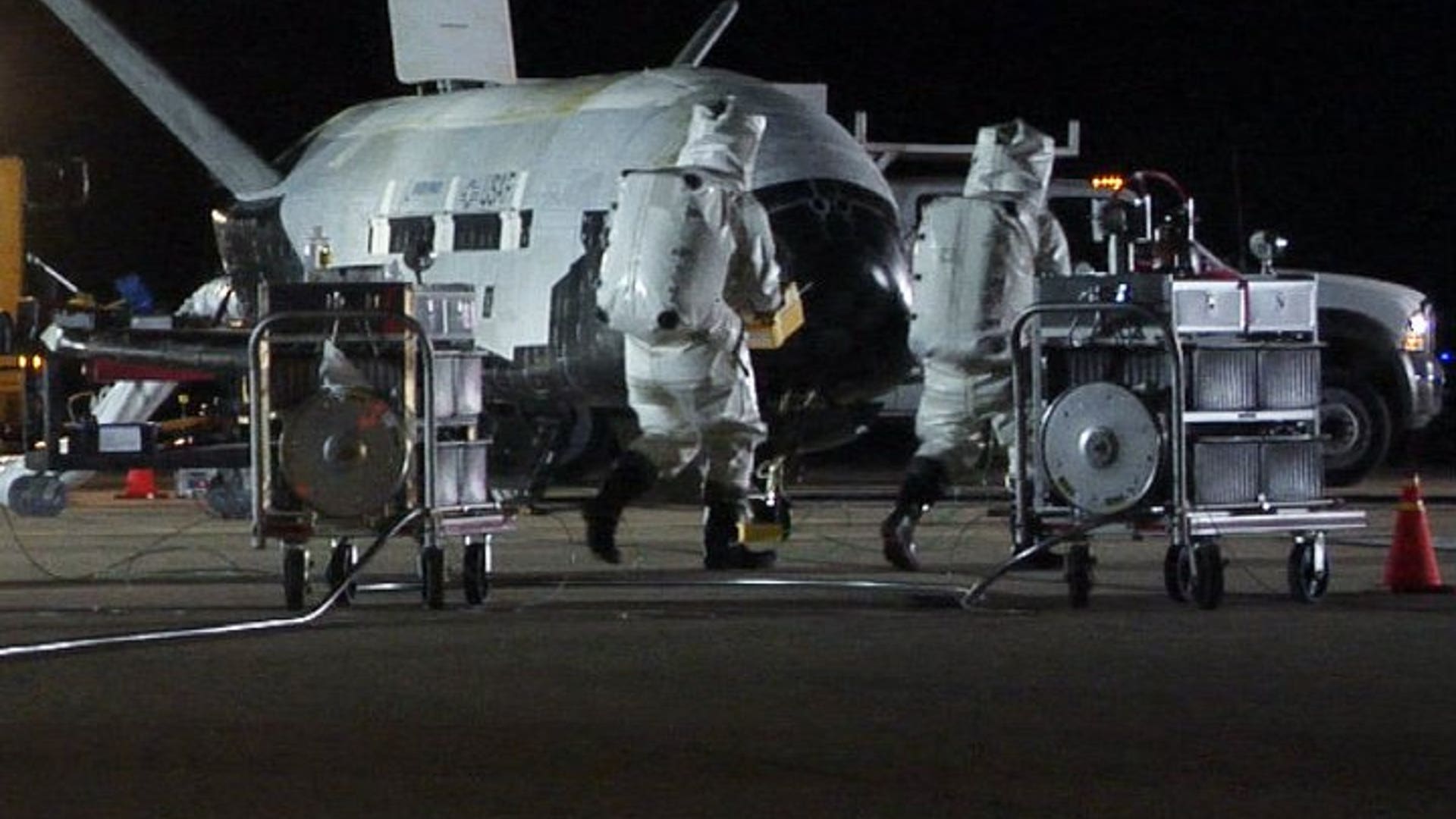
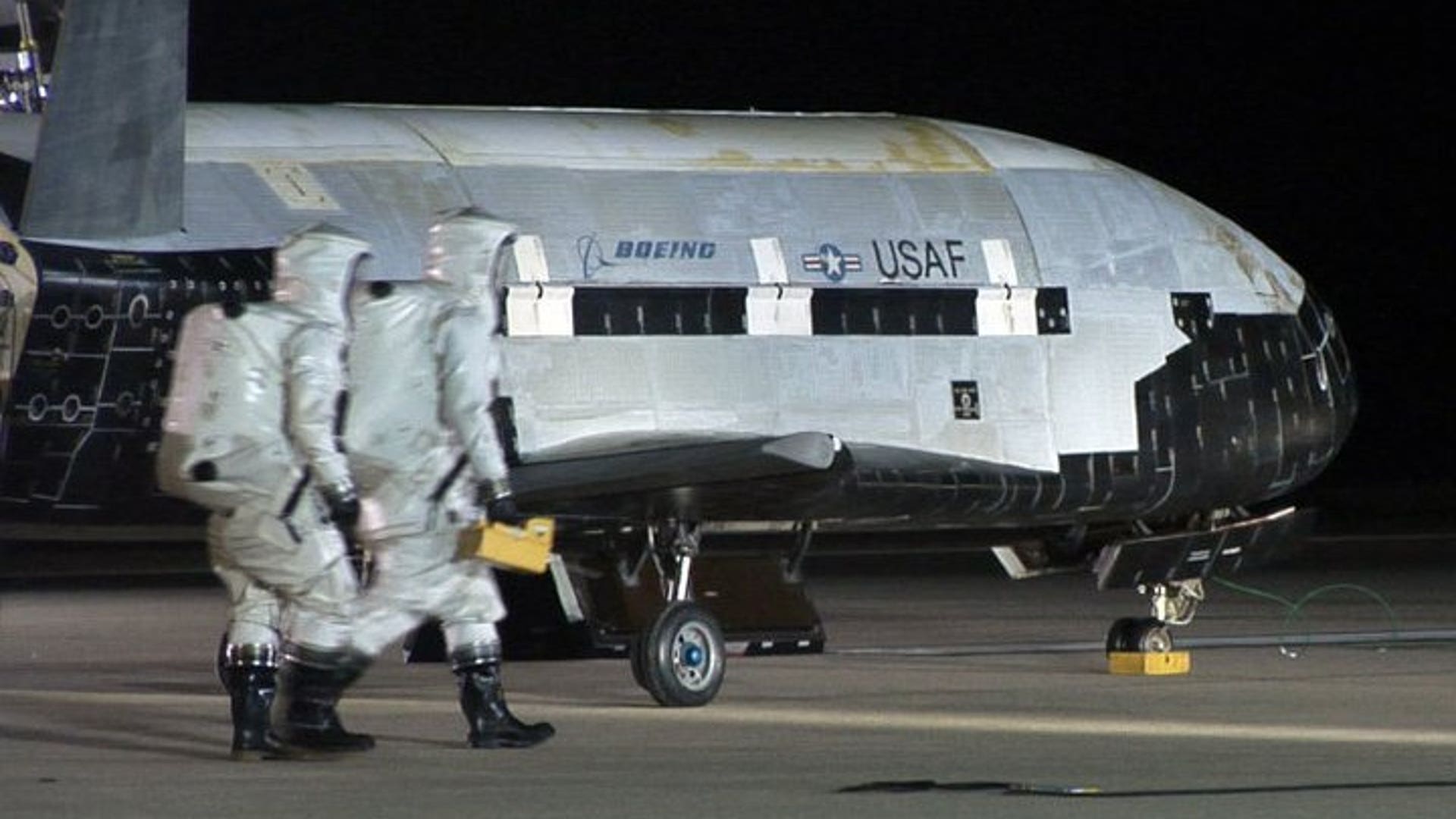
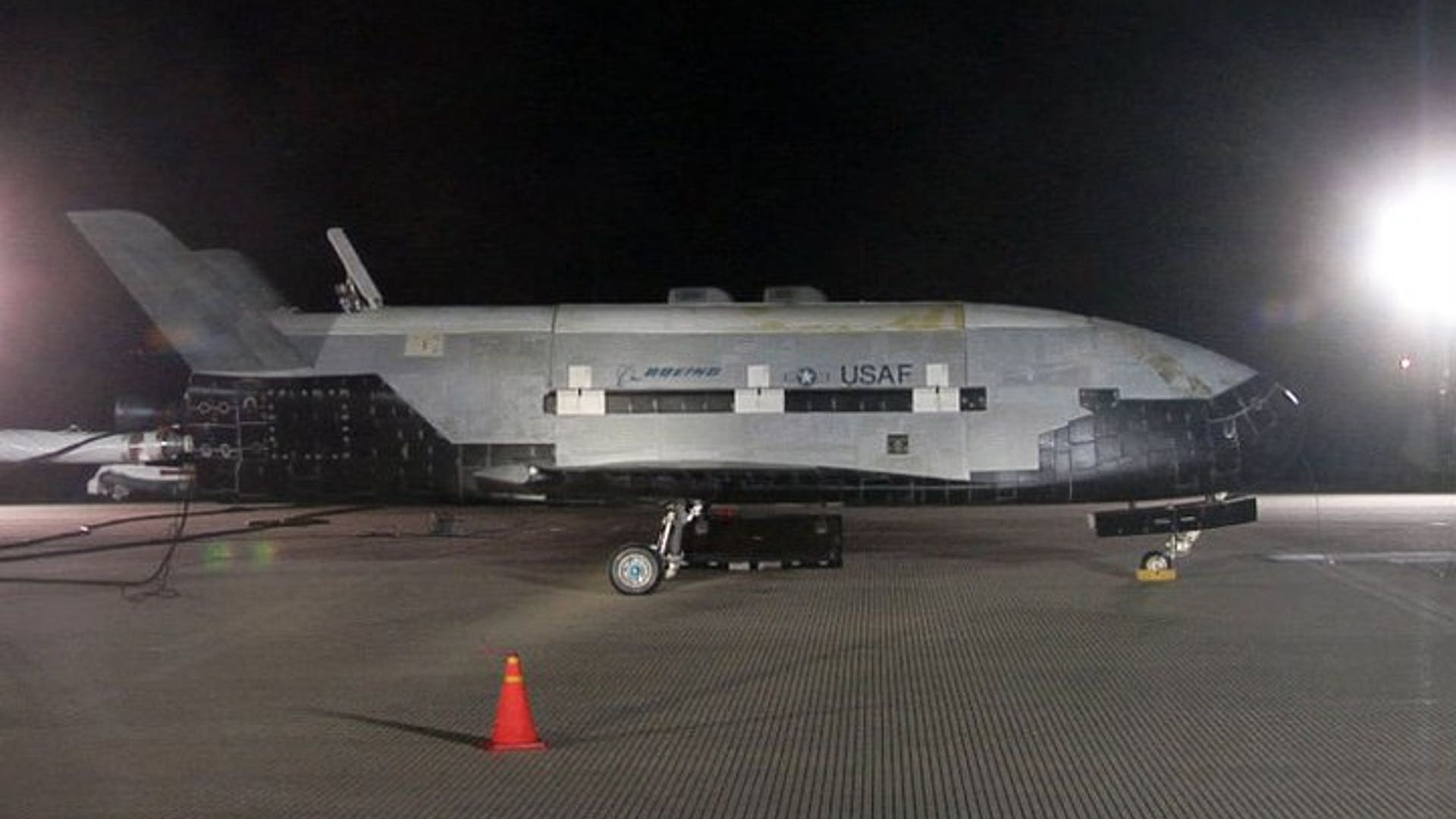
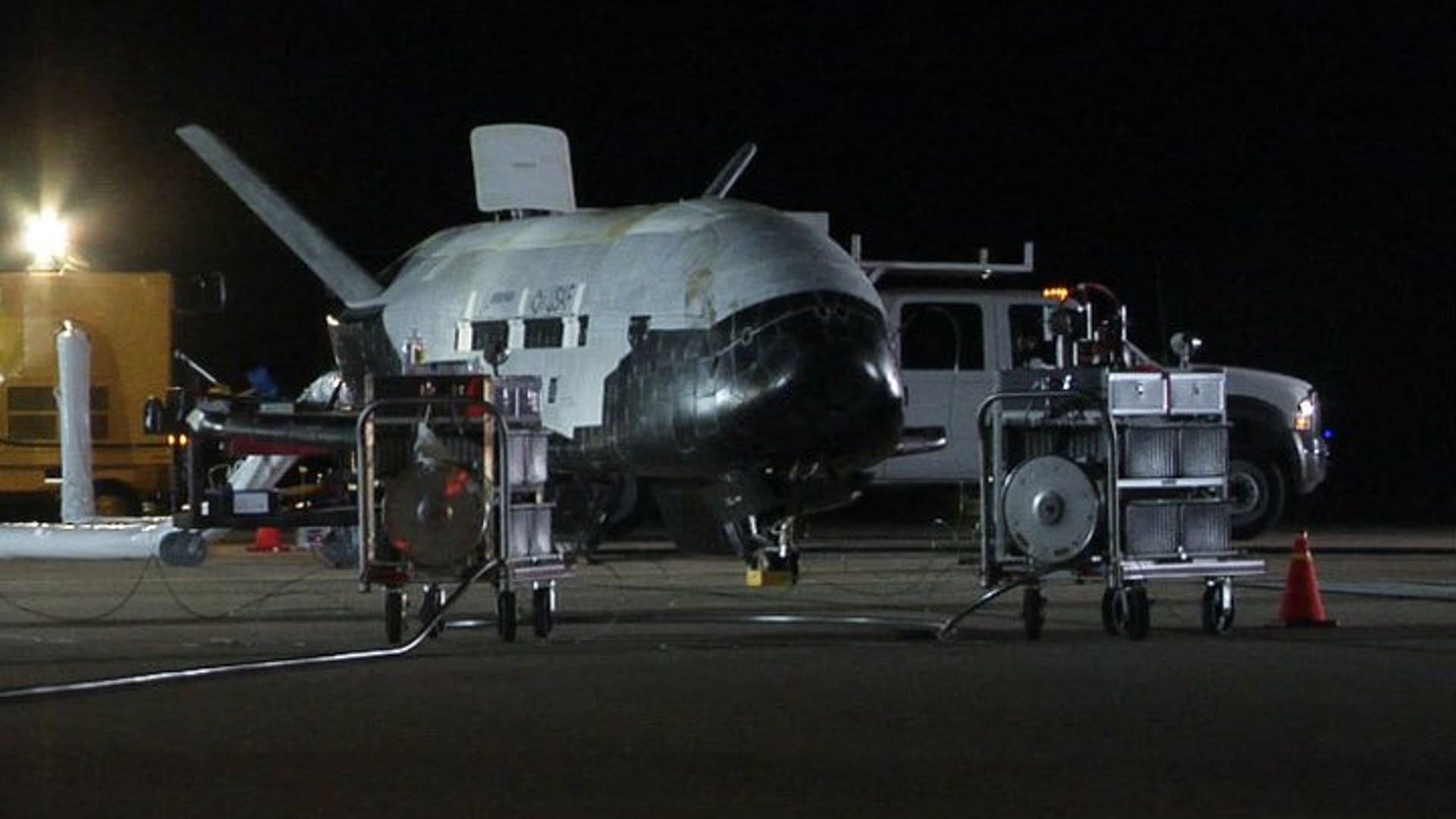
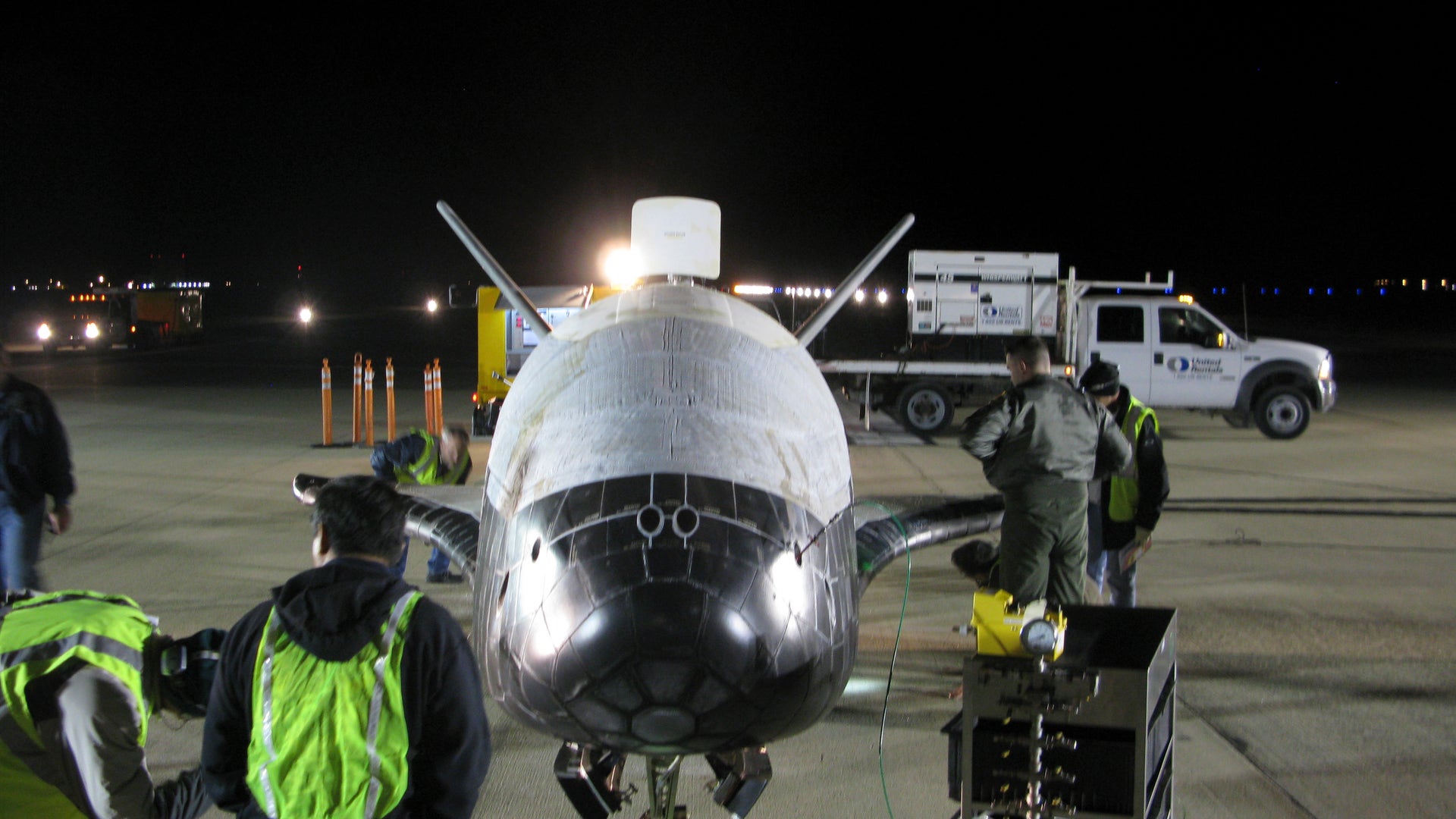
![NASA's X-37B Lands]() The Air Force has not said whether it carried anything in its cargo bay, but insists the primary purpose of the mission was to test the craft itself. "We are very pleased that the program completed all the on-orbit objectives for the first mission," program manager Lt. Col. Troy Giese said in a statement.read moreUSAF / Vandenberg AFBShare
The Air Force has not said whether it carried anything in its cargo bay, but insists the primary purpose of the mission was to test the craft itself. "We are very pleased that the program completed all the on-orbit objectives for the first mission," program manager Lt. Col. Troy Giese said in a statement.read moreUSAF / Vandenberg AFBShare![NASA's X-37B Lands]()
![NASA's X-37B Lands]()
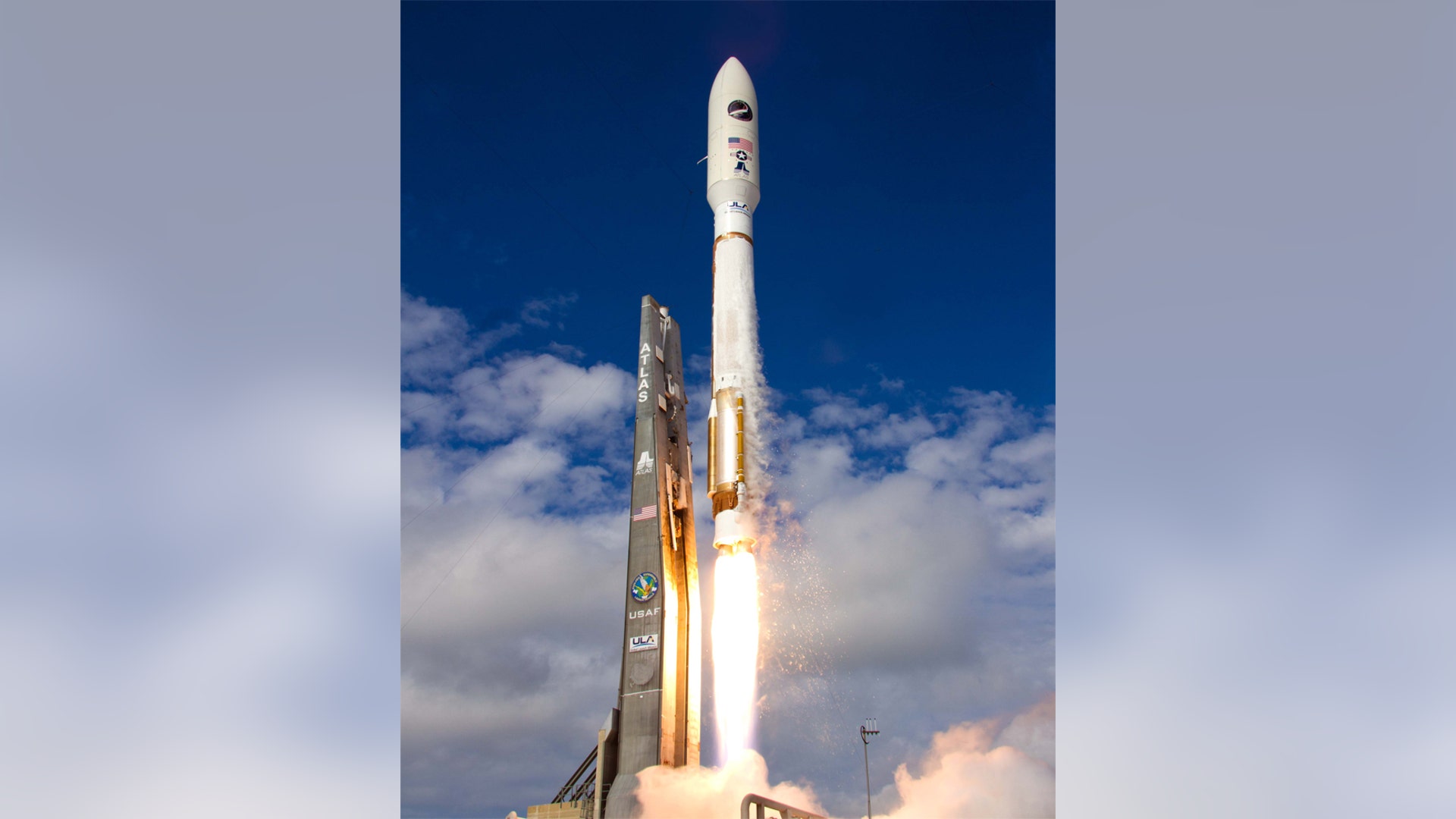
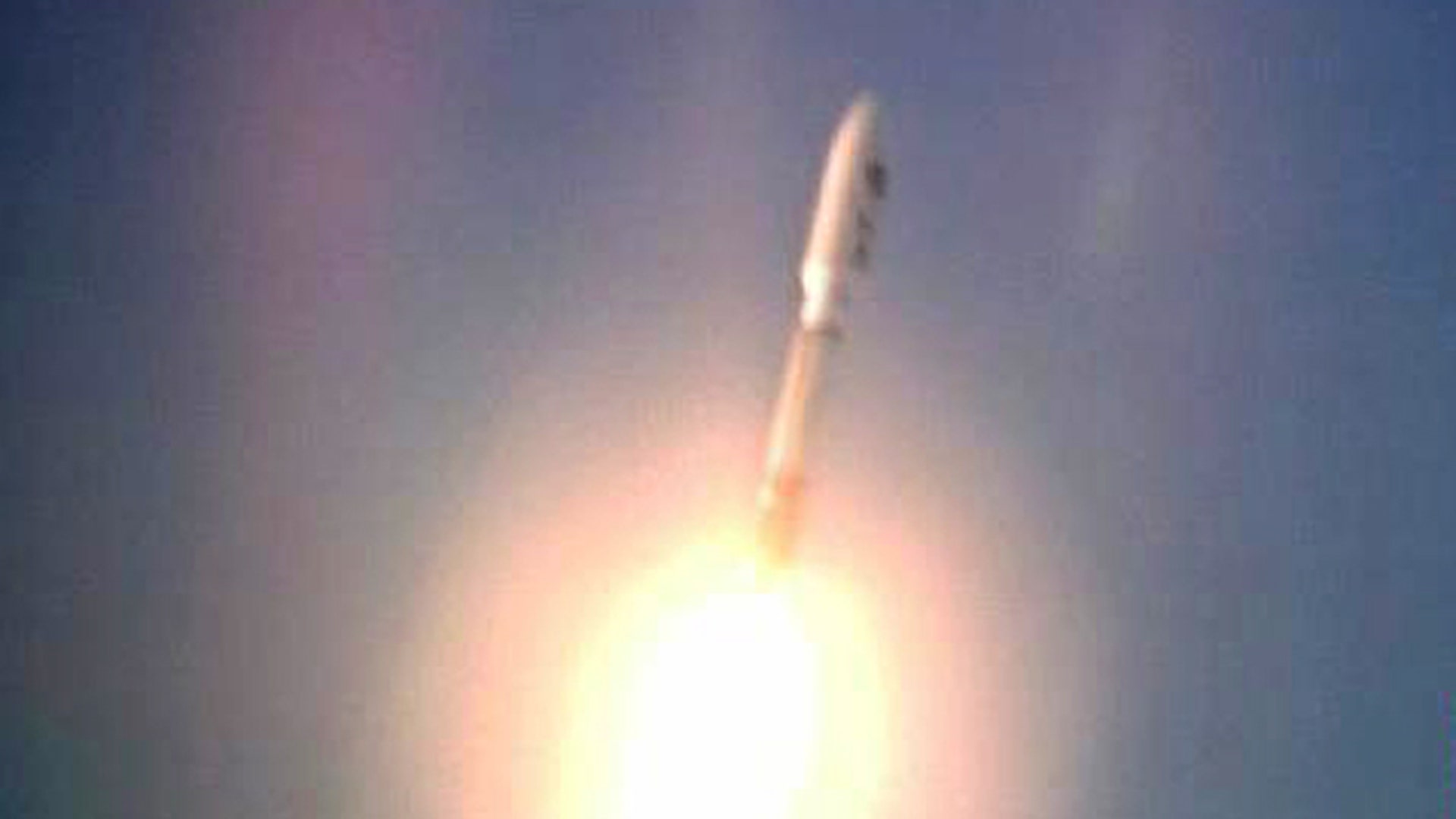
![Air_Force_Rocket_Launch]()
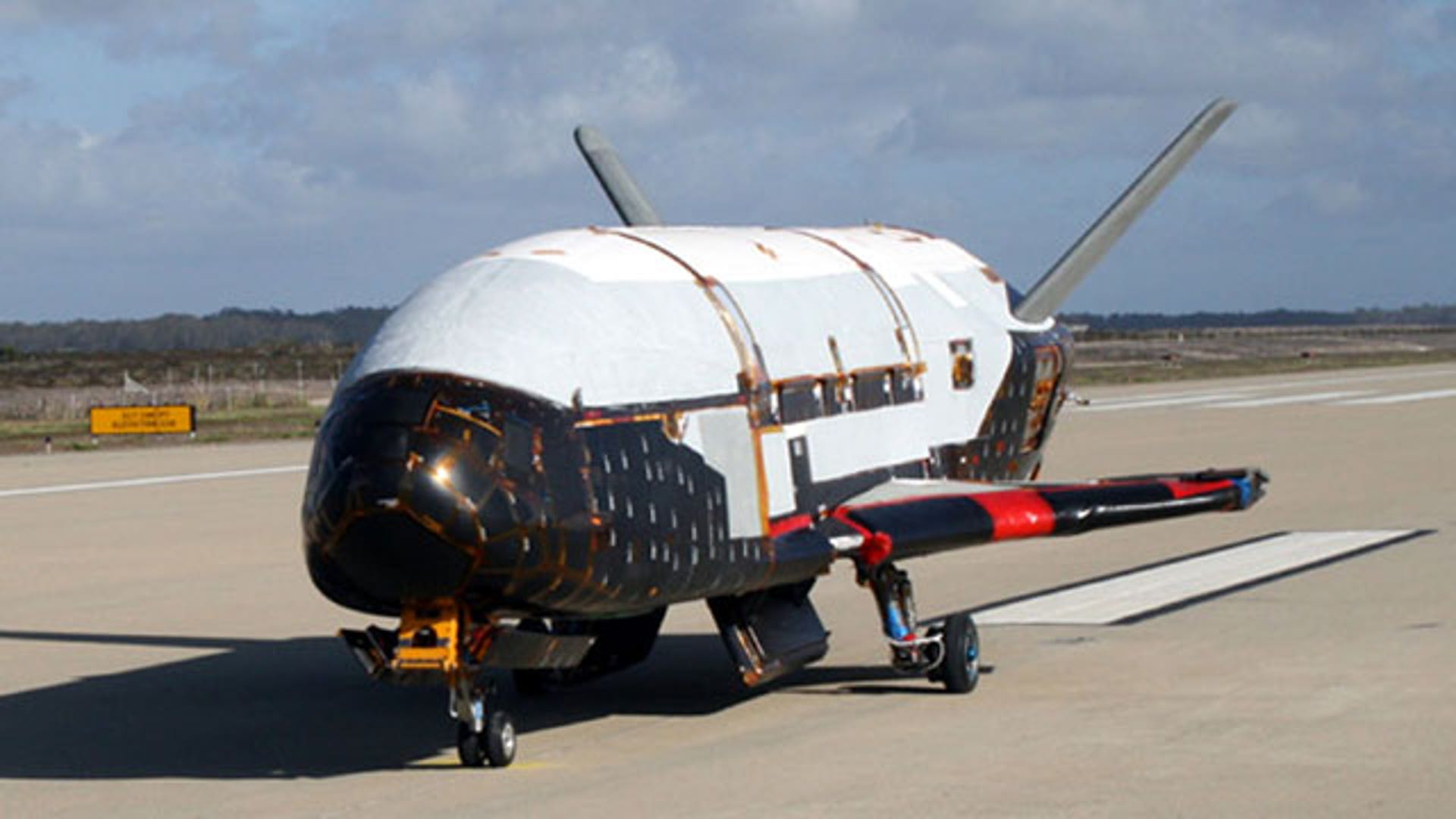
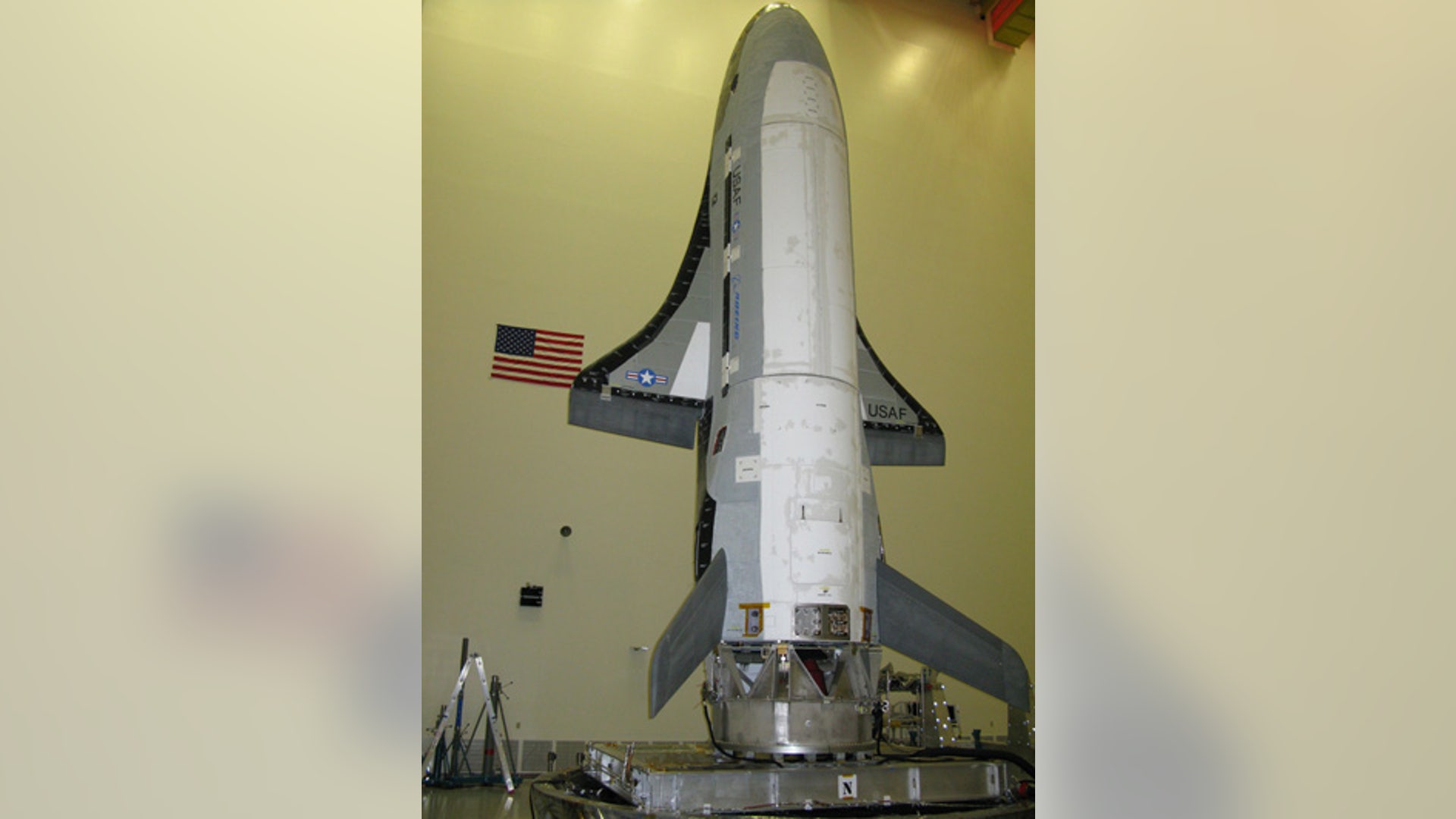
![Air Force X-37B]() This undated image released by the U.S. Air Force shows the X-37B spacecraft, which got a boost into orbit from Florida on April 22. The reusable robotic X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle is a small space shuttle-like craft. The craft will wing its way into Earth orbit, remain aloft for an unspecified time, then high-tail its way back down to terra-firma -- auto-piloting down to a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.read moreAPShare
This undated image released by the U.S. Air Force shows the X-37B spacecraft, which got a boost into orbit from Florida on April 22. The reusable robotic X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle is a small space shuttle-like craft. The craft will wing its way into Earth orbit, remain aloft for an unspecified time, then high-tail its way back down to terra-firma -- auto-piloting down to a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.read moreAPShare![X-37B Overview]()
![Hiding in a Rocket]()
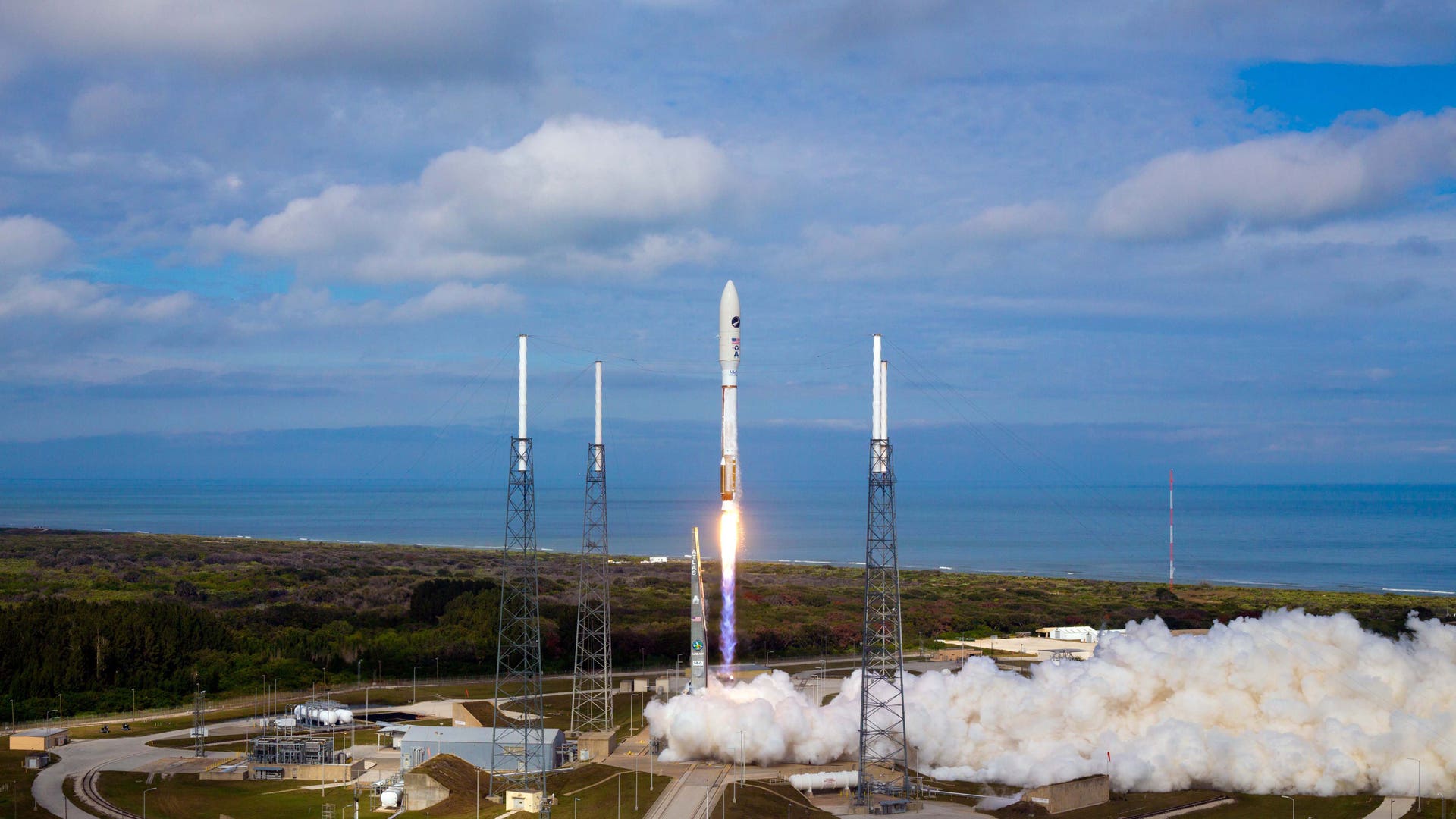
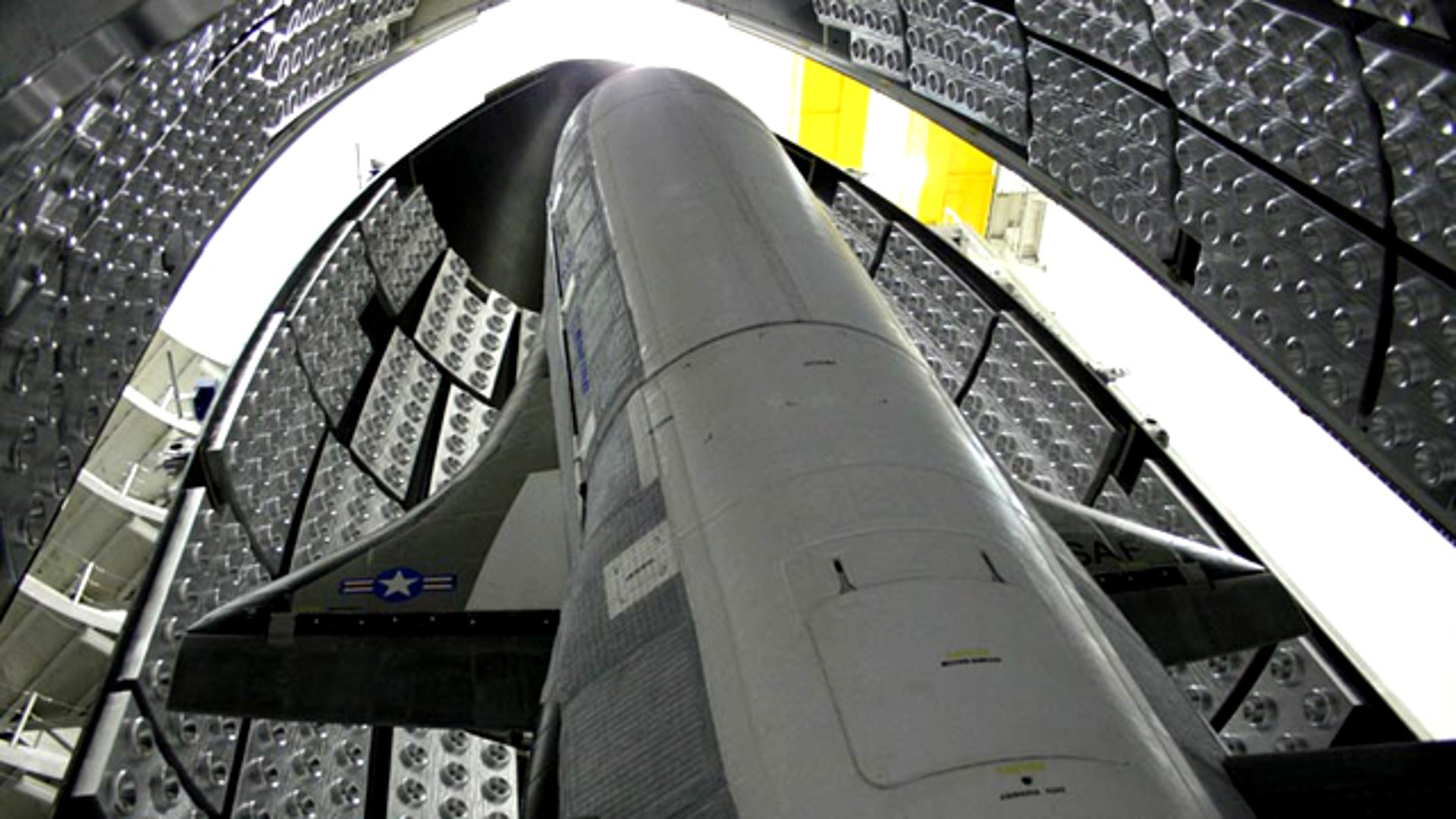
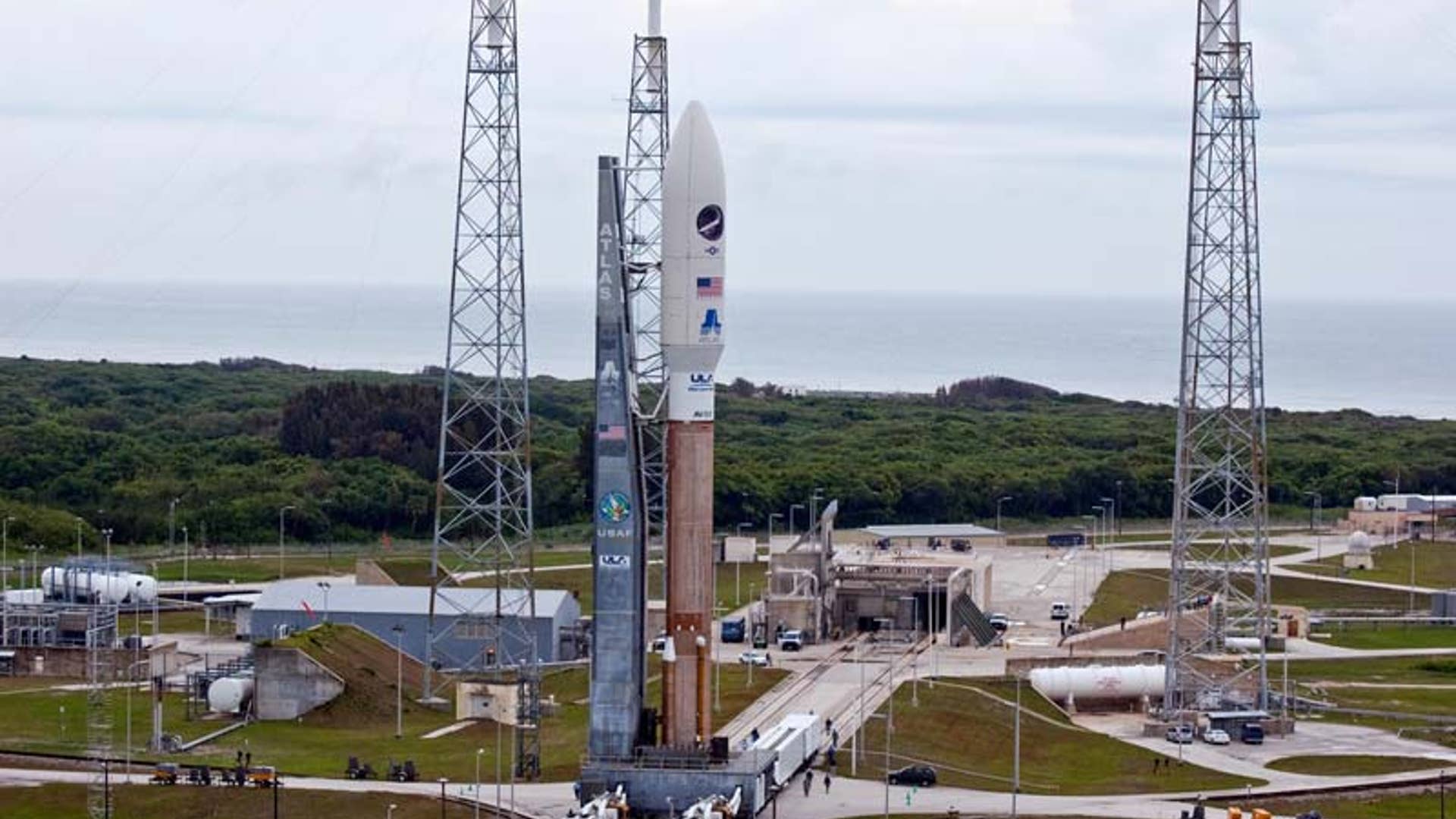
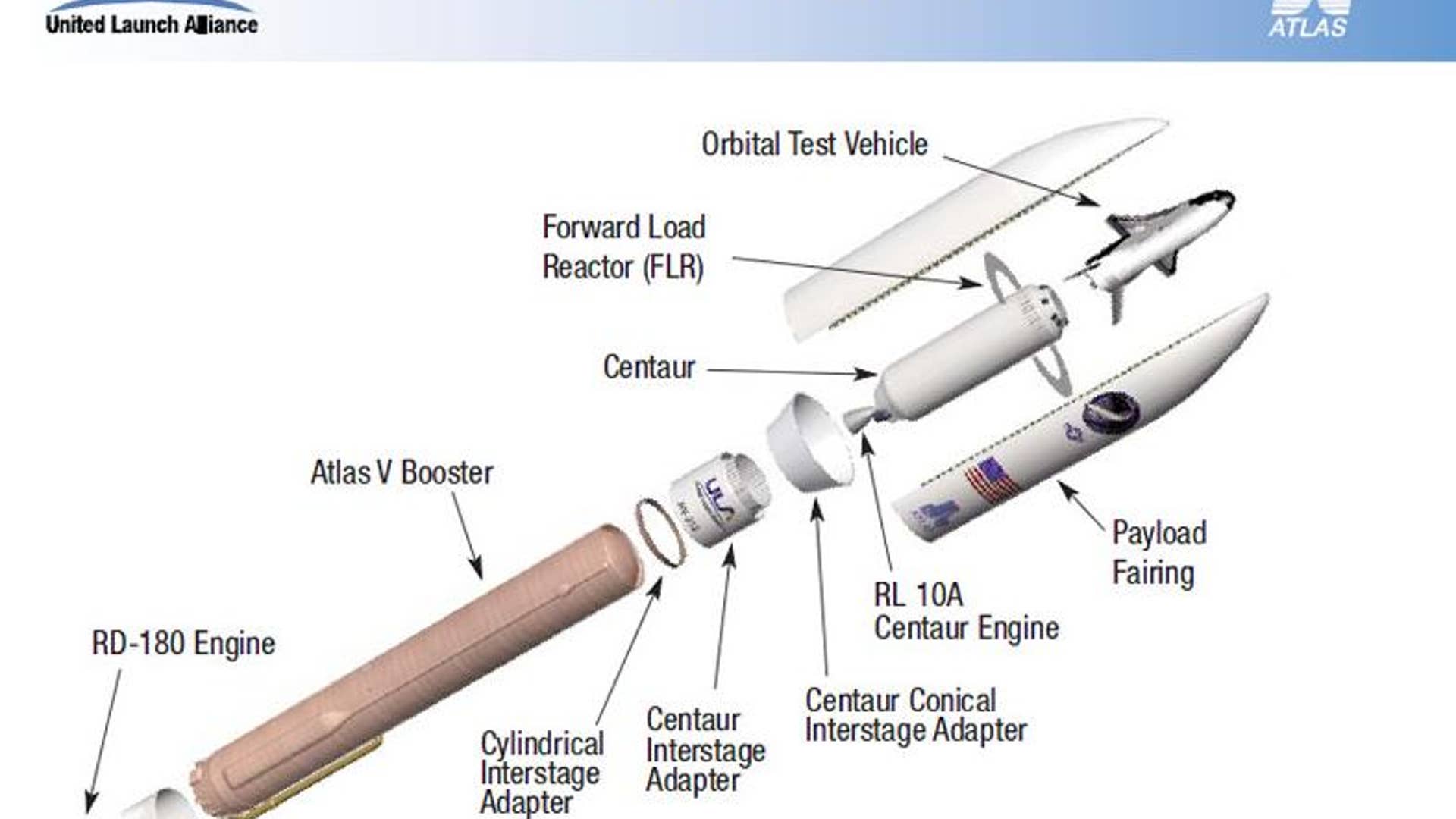
![X-37B on Launchpad]() A United Launch Alliance Atlas 5 rocket with the Air Force's X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV) -- inside the bulbous nose cone -- the rolls out to its Space Launch Complex-41 launch pad at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on April 21, 2010.read morePat Corkery/United Launch AllianceShare
A United Launch Alliance Atlas 5 rocket with the Air Force's X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV) -- inside the bulbous nose cone -- the rolls out to its Space Launch Complex-41 launch pad at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on April 21, 2010.read morePat Corkery/United Launch AllianceShare![Atlas_Launch_Plans]()
![Final Test for X-37B]()
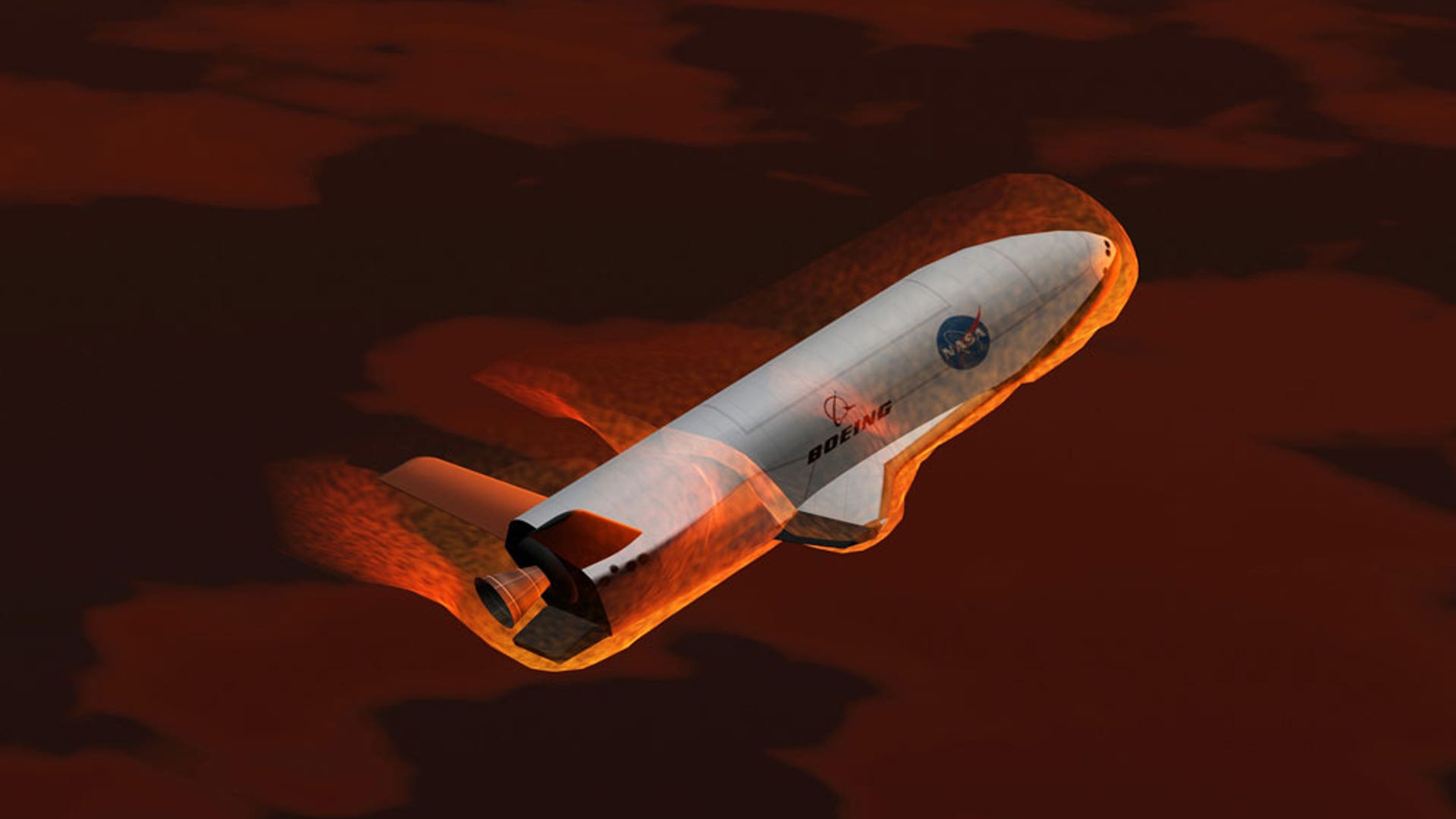
![Secret_Flight7]() Artist's conception of the X-37 advanced technology flight demonstrator re-entering Earth's atmosphere. The X-37 will be a testbed for dozens of advanced structural, propulsion and operational technologies that could dramatically lower the cost of future reusable launch vehicles. The X-37 will operate in both the orbital and reenty phases of flight. The X-37 measures approximately 27.5 feet long and 15 feet in wingspan. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala., manages the X-37 project. The X-37 industry team is led by The Boeing Co. of Seal Beach, Calif. Source: NASA/MSFCread more
Artist's conception of the X-37 advanced technology flight demonstrator re-entering Earth's atmosphere. The X-37 will be a testbed for dozens of advanced structural, propulsion and operational technologies that could dramatically lower the cost of future reusable launch vehicles. The X-37 will operate in both the orbital and reenty phases of flight. The X-37 measures approximately 27.5 feet long and 15 feet in wingspan. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala., manages the X-37 project. The X-37 industry team is led by The Boeing Co. of Seal Beach, Calif. Source: NASA/MSFCread more![Secret_Flight2]()
![Secret_Flight6]() Illustration of the X-37 Advanced Technology Demonstrator during flight. As a mini-space plane, this Boeing Phantom Works craft has been under development for years. Several agencies have been involved in the effort, NASA as well as the Defense Advanced Projects Research Agency (DARPA) and various arms of the U.S. Air Force. Source: NASAread more
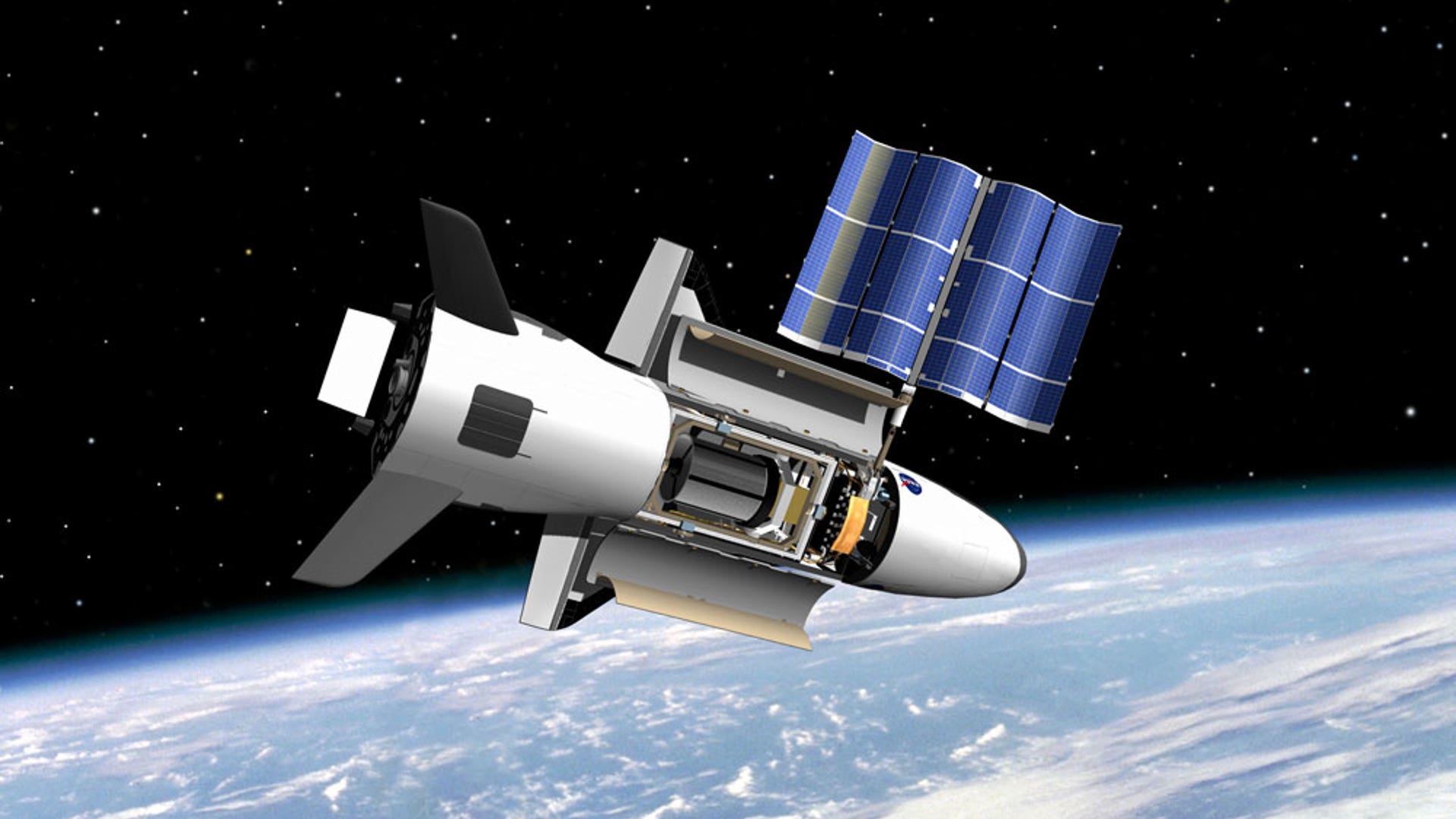
Illustration of the X-37 Advanced Technology Demonstrator during flight. As a mini-space plane, this Boeing Phantom Works craft has been under development for years. Several agencies have been involved in the effort, NASA as well as the Defense Advanced Projects Research Agency (DARPA) and various arms of the U.S. Air Force. Source: NASAread more![Secret_Flight5]() Illustration of the X-37 Advanced Technology Demonstrator in STS cargo bat. Once in orbit, what such a vehicle might enable depends on the eye of the beholder. Intelligence gathering, kicking off small satellites, testing space gear are feasible duties, as is developing reusable space vehicle technologies. Source: NASAread more
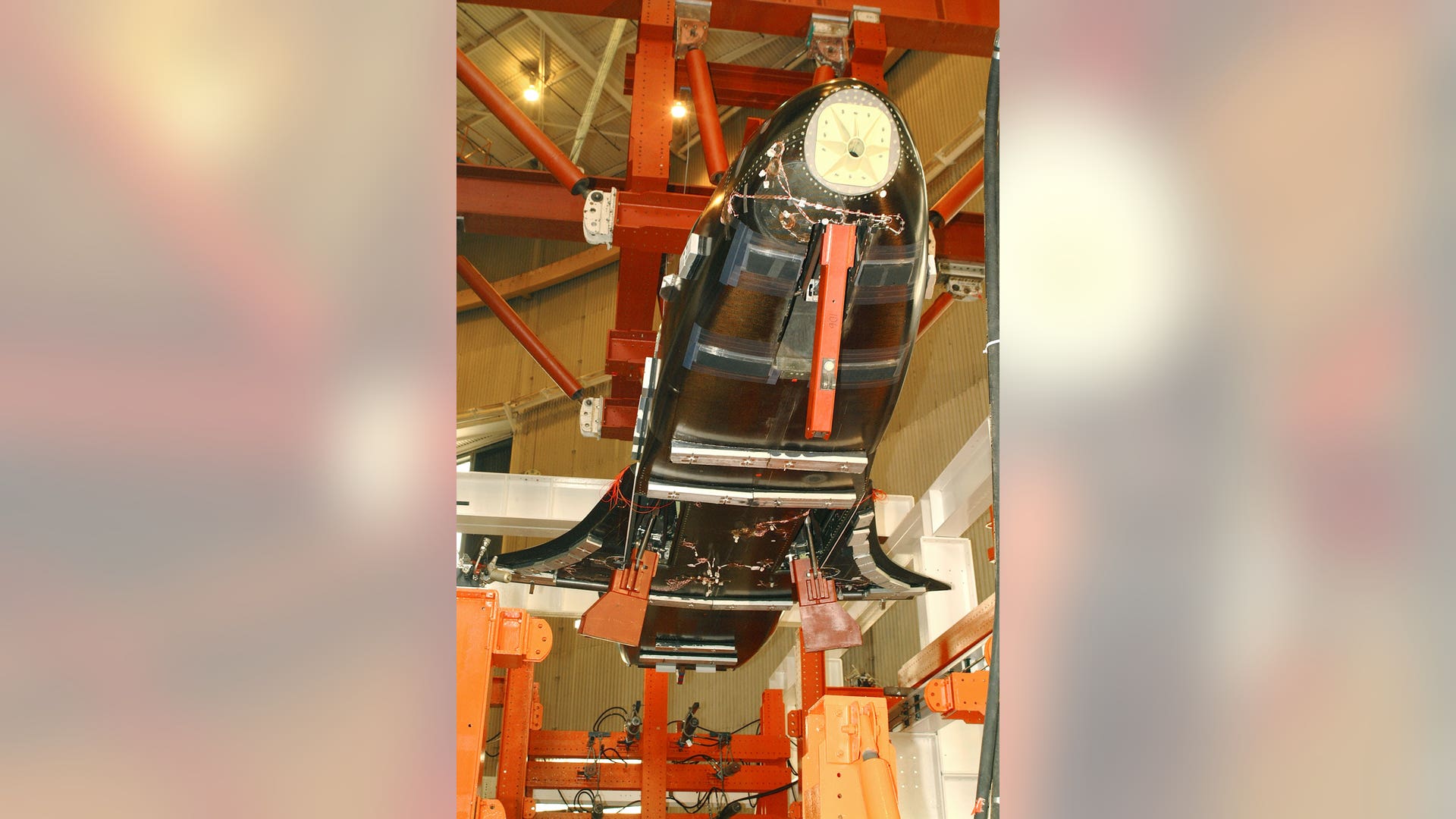
Illustration of the X-37 Advanced Technology Demonstrator in STS cargo bat. Once in orbit, what such a vehicle might enable depends on the eye of the beholder. Intelligence gathering, kicking off small satellites, testing space gear are feasible duties, as is developing reusable space vehicle technologies. Source: NASAread more![Secret_Flight1]() NASA's X-37 Approach and Landing Test Vehicle is installed in a structural test facility at Boeing's Huntington Beach, Calif., plant. The tests, which were completed in July 2003, were conducted to verify the structural integrity of the vehicle in preparation for atmospheric flight tests. The X-37 is a flight demonstrator project to flight test advancing technologies for NASA's Orbital Space Plane Program. Source: Boeing/R. Davisread more
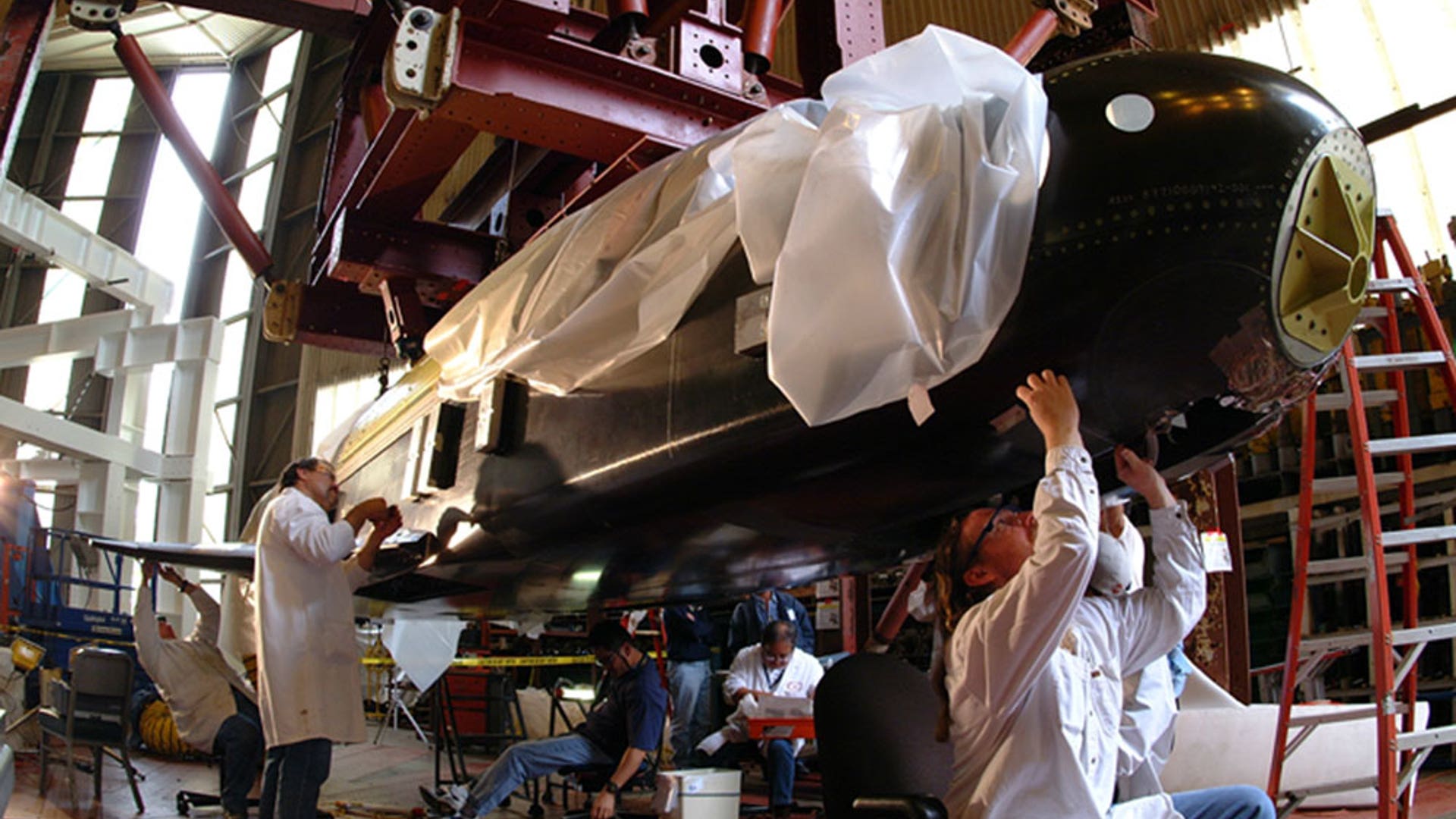
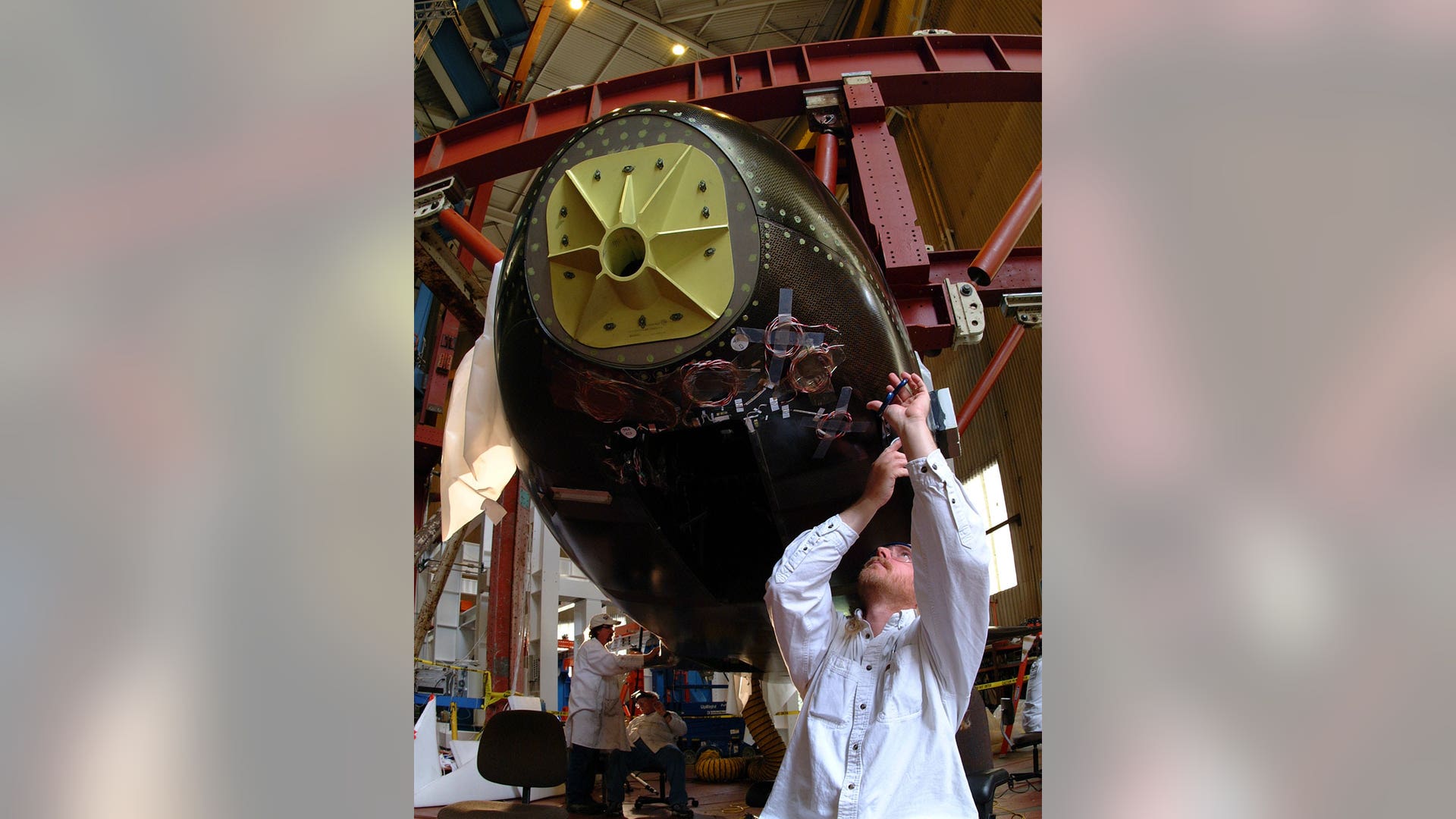
NASA's X-37 Approach and Landing Test Vehicle is installed in a structural test facility at Boeing's Huntington Beach, Calif., plant. The tests, which were completed in July 2003, were conducted to verify the structural integrity of the vehicle in preparation for atmospheric flight tests. The X-37 is a flight demonstrator project to flight test advancing technologies for NASA's Orbital Space Plane Program. Source: Boeing/R. Davisread more![Secret_Flight3]() A Boeing technician makes adjustments to composite panels on NASA's X-37 Approach and Landing Test Vehicle in preparation for structural testing at Boeing's Huntington Beach, Calif., plant. The proof tests to validate the structural integrity of the airframe were successfully completed in July 2003. Technologies demonstrated will aid in the design of the Orbital Space Plane. Source: Boeing/R. Davisread more
A Boeing technician makes adjustments to composite panels on NASA's X-37 Approach and Landing Test Vehicle in preparation for structural testing at Boeing's Huntington Beach, Calif., plant. The proof tests to validate the structural integrity of the airframe were successfully completed in July 2003. Technologies demonstrated will aid in the design of the Orbital Space Plane. Source: Boeing/R. Davisread more![Secret_Flight4]() Boeing technicians at the Huntington Beach plant make adjustments to composite panels on NASA's X-37 Approach and Landing Test Vehicle prior to proof tests to validate the airframe structure. The X-37 is an advanced technology flight demonstrator designed to test technologies for the Orbital Space Plane Program. Source: Boeing/R. Davisread more
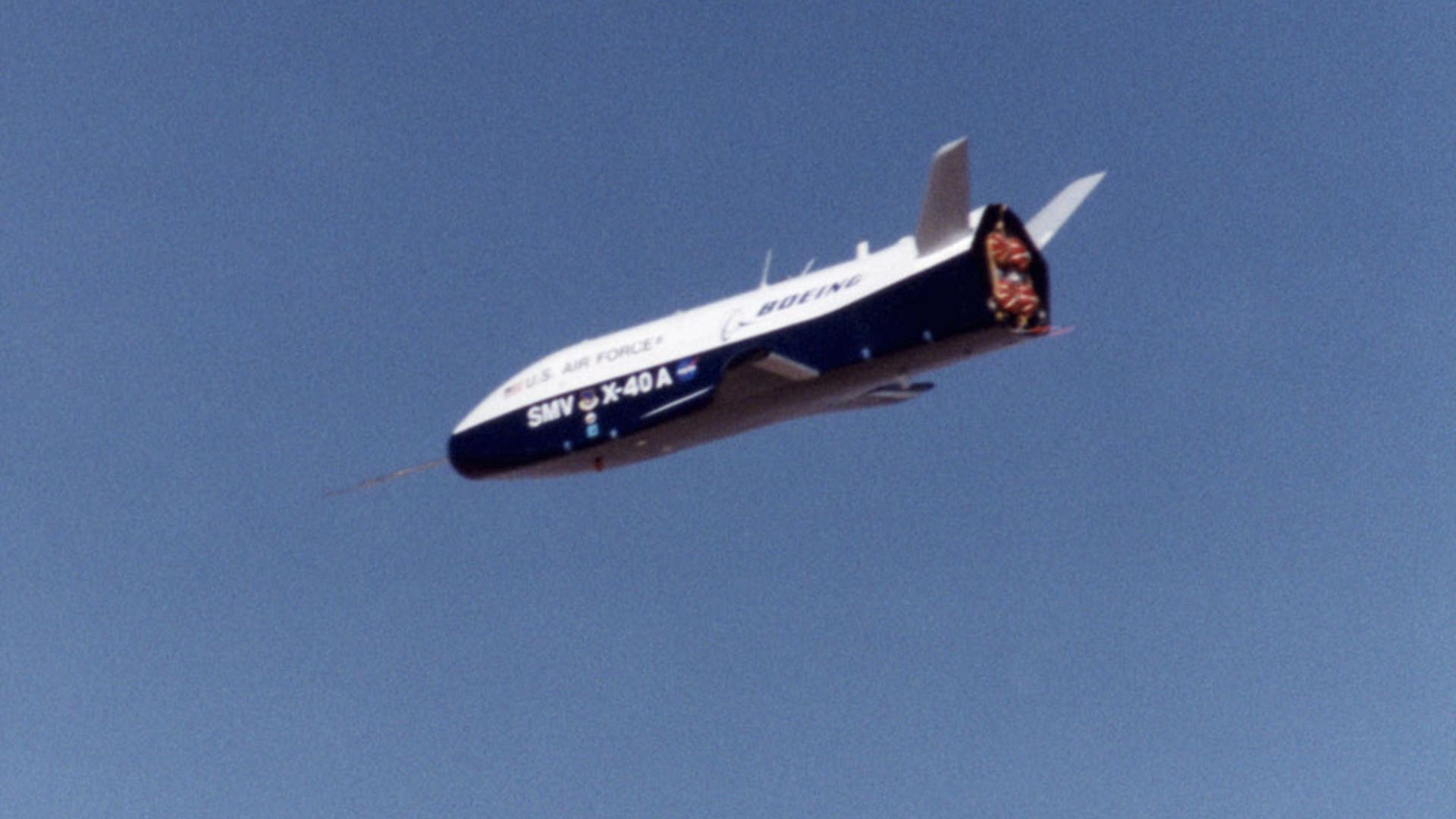
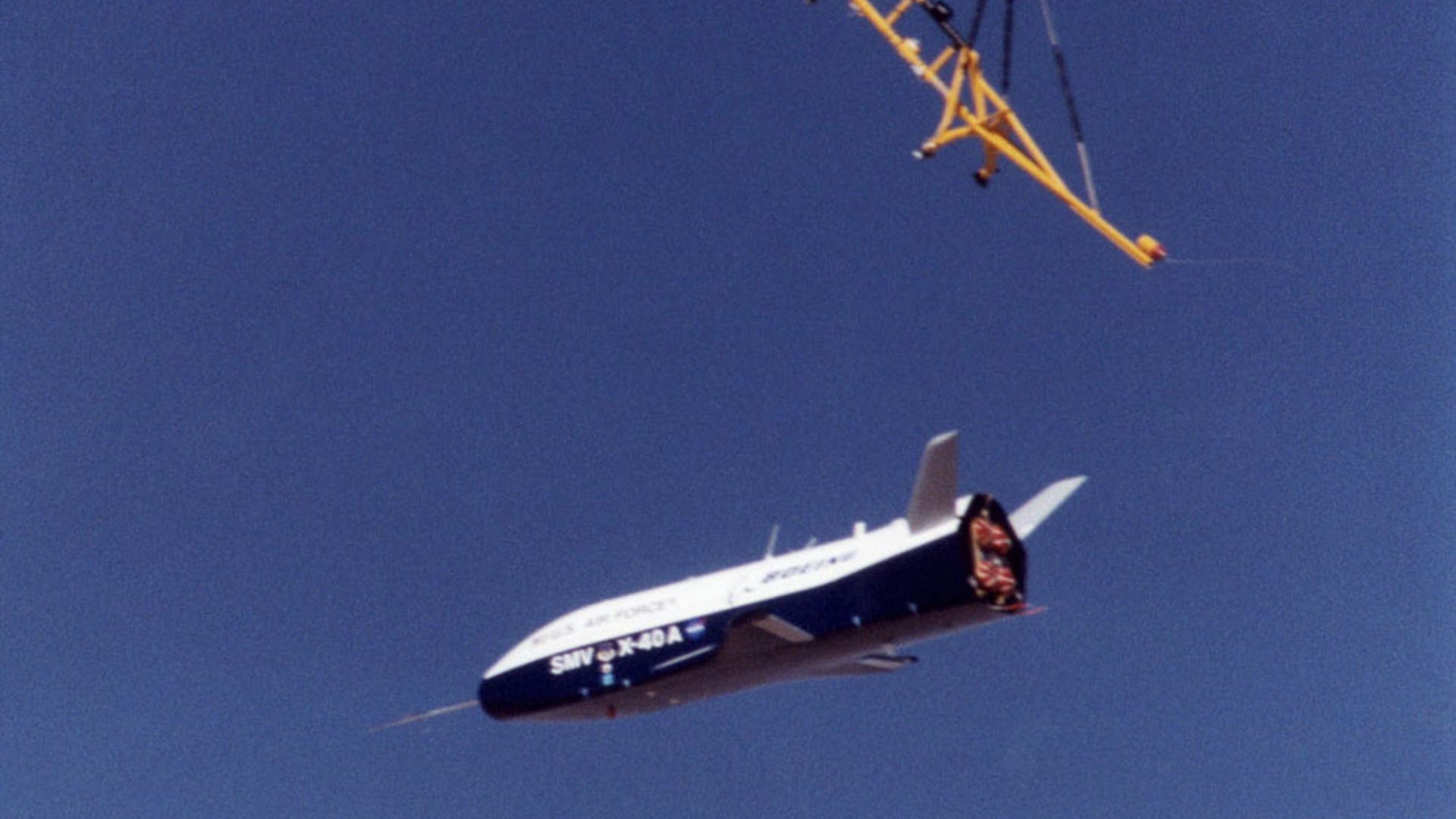
Boeing technicians at the Huntington Beach plant make adjustments to composite panels on NASA's X-37 Approach and Landing Test Vehicle prior to proof tests to validate the airframe structure. The X-37 is an advanced technology flight demonstrator designed to test technologies for the Orbital Space Plane Program. Source: Boeing/R. Davisread more![Secret_Flight9]() The unpowered, unpiloted X-40A vehicle is an 85 percent scale, risk-reduction version of the proposed X-37 flight demonstrator. In 2001, the X-40A proved the capability of an autonomous flight control and landing system in a series of flight tests at NASA'a Dryden Flight Research Center. Ultimately, the unpiloted X-37 is intended as an orbital testbed and technology demonstrator, capable of landing like an airplane and being quickly serviced for a follow-up mission. Source: NASAread more
The unpowered, unpiloted X-40A vehicle is an 85 percent scale, risk-reduction version of the proposed X-37 flight demonstrator. In 2001, the X-40A proved the capability of an autonomous flight control and landing system in a series of flight tests at NASA'a Dryden Flight Research Center. Ultimately, the unpiloted X-37 is intended as an orbital testbed and technology demonstrator, capable of landing like an airplane and being quickly serviced for a follow-up mission. Source: NASAread more![Secret_Flight10]() X-40A's first flight was a 74 second glidef from 15,000 feet on March 14, 2001. Each of the seven flights were successfully completed. The unpiloted X-40 is a risk-reduction vehicle for the X-37, which is intended to be a reusable space vehicle. The X-37 is designed to demonstrate technologies in the orbital and reentry environments for next-generation reusable launch vehicles that will increase both safety and reliability, while reducing launch costs from $10,000 per pound to $1,000 per pound. Source: NASAread more
X-40A's first flight was a 74 second glidef from 15,000 feet on March 14, 2001. Each of the seven flights were successfully completed. The unpiloted X-40 is a risk-reduction vehicle for the X-37, which is intended to be a reusable space vehicle. The X-37 is designed to demonstrate technologies in the orbital and reentry environments for next-generation reusable launch vehicles that will increase both safety and reliability, while reducing launch costs from $10,000 per pound to $1,000 per pound. Source: NASAread more![Secret_Flight11]()
![Secret_Flight12]()
- Published27 Images
Inside the Air Force's secret space plane
The U.S. Air Force launched the robotic X-37B space plane in early 2010 on a space mission that remains a secret -- even after the craft touched ground 225 days later at Vandenberg Air Force Base. In early 2011, the ship took off again on its latest mission.
Move Forward
- Inside the Air Force's secret space plane



























Thumbnail View
Image 0 of 27