How to forward voicemails on iPhone and Android
Have you ever wondered whether you can forward a voicemail to someone else? Kurt "The CyberGuy" Knutsson explains how you can share the audio message on iPhone and Android.
In an alarming revelation, Bitdefender Labs has uncovered a sinister turn in cybercrime tactics on Facebook. Hackers are using a new virus called NodeStealer to steal your cookies and passwords. It’s a sneaky piece of code that runs on JavaScript and Node.js, and it can grab your web browser data and use it to hack into your Facebook account.
How NodeStealer works
How do they do it? Well, they use cunning malvertising campaigns, which are fake ads that look like they’re from Meta, the company that owns Facebook. When you click on these ads, you’re actually downloading the NodeStealer virus, which then starts to spy on your online activity.
NodeStealer is a virus that seeks to steal information, like passwords, from Facebook users. (Credit: Bitdefender Labs)
MORE: DON'T FALL FOR THAT "LOOK WHO DIED" FACEBOOK MESSAGE TRAP
Provocative lure tricks people who are using Facebook
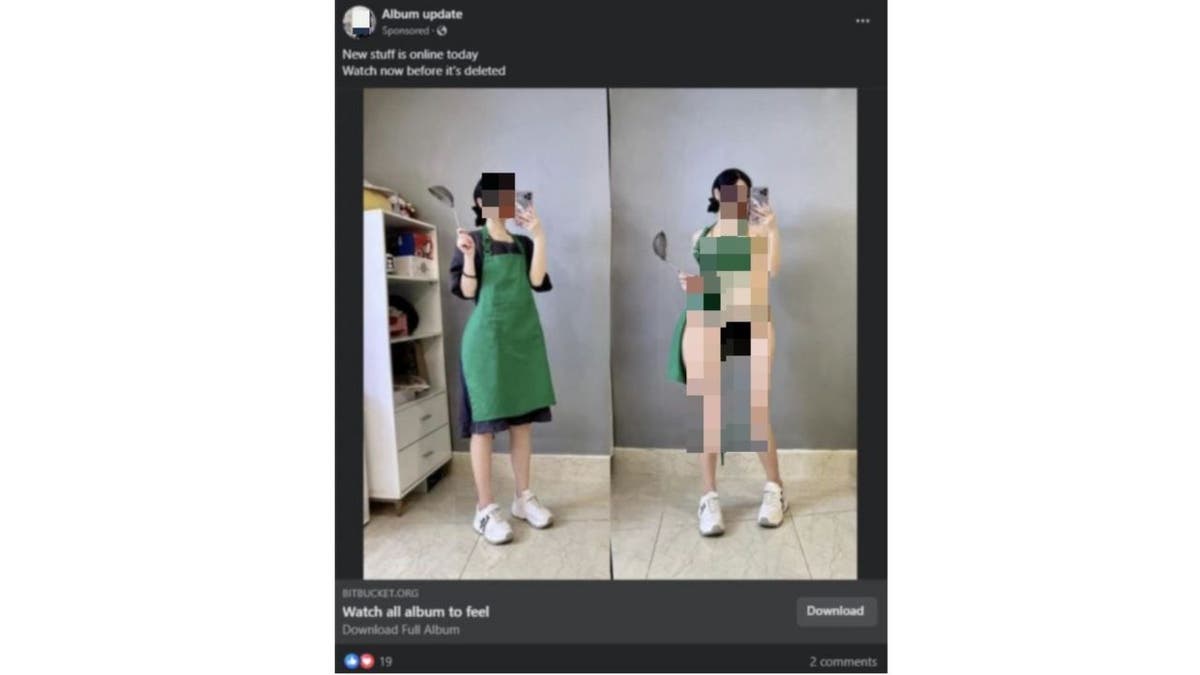
Hackers will post ads on Facebook with pictures of pretty girls, hoping to get you to click on them. But don’t fall for it. These ads are actually hiding a nasty virus that can steal your passwords and personal information.
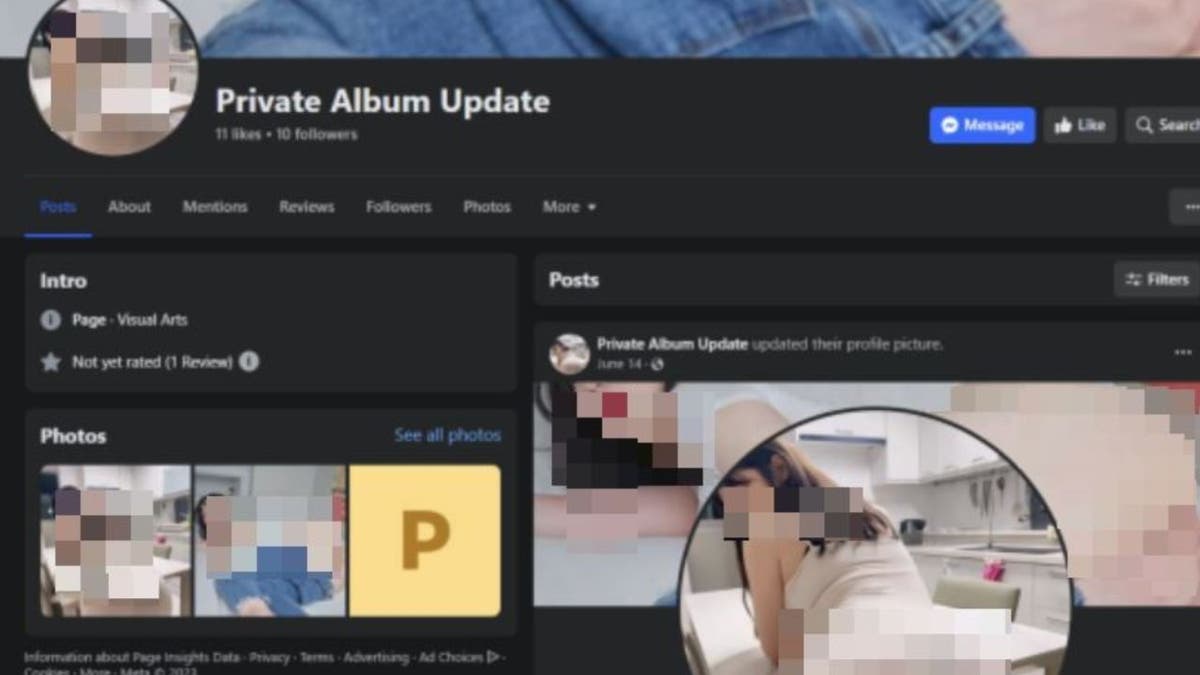
Bitdefender researchers found that at least 10 Facebook accounts that belong to businesses have been hacked and used to spread these ads. The ads have a link that says, "Photo Album," but when you click on it, you download a file that infects your computer. The file then gets access to your browser cookies and passwords, which lets the hackers get into your accounts.
MORE: DON'T FALL FOR THAT "LOOK WHO DIED" FACEBOOK MESSAGE TRAP
Hackers post ads with women on Facebook in an attempt to lure people into clicking on them, thereby stealing their information. (Credit: Bitdefender Labs)
MORE: FOOLPROOF STEPS TO HELP PROTECT YOUR FACEBOOK ACCOUNT FROM HACKERS
Disturbing spread of this attack
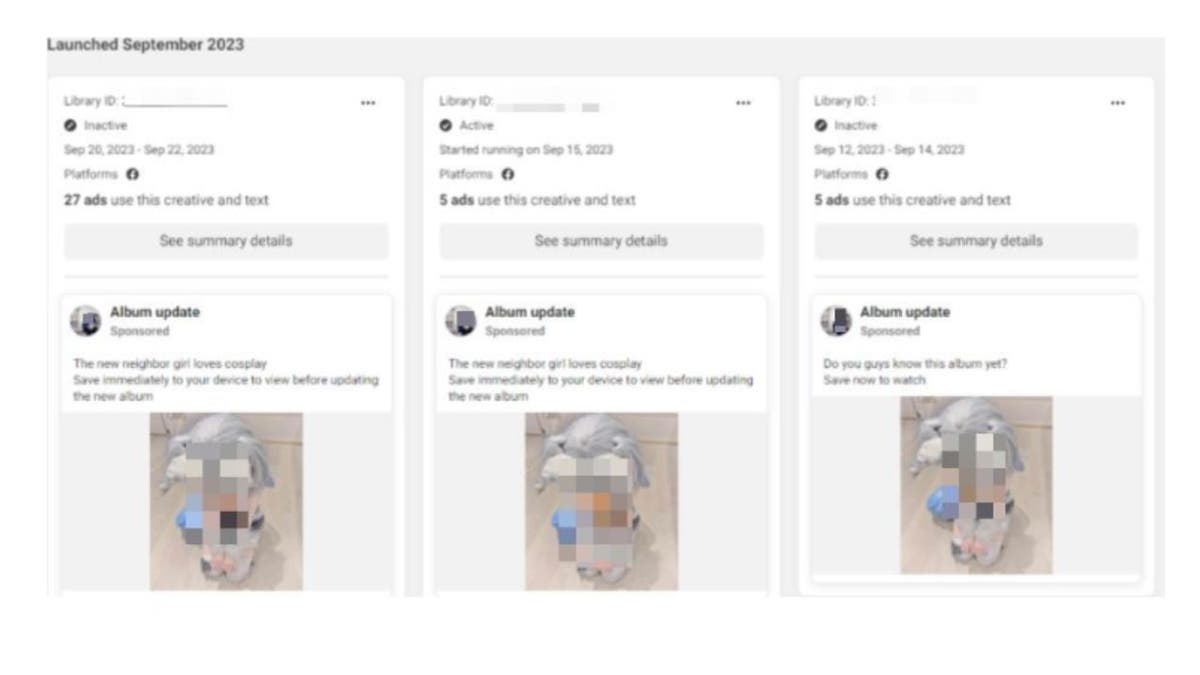
The sheer reach of these campaigns is deeply concerning. Bitdefender's analysis estimates an astounding 100,000 potential downloads, with a single ad amassing up to 15,000 downloads within a mere 24-hour span. Demographically, males over 45 are the most impacted, highlighting the targeted nature of these attacks.
HOW TO FORWARD A VOICEMAIL FROM ANY SMARTPHONE
Males over 45 are most impacted by this malware campaign. (Credit: Bitdefender Labs)
MORE: DON'T FALL FOR THIS SNEAKY NOTIFICATION THAT'S FOOLING PEOPLE ON FACEBOOK AND INSTAGRAM
How the Facebook ad malware threat is evolving into more elusive trouble
Originally identified by Meta's security team in early 2023, NodeStealer has undergone a rapid and troubling transformation. The malware, initially devised to steal browser cookies and execute large-scale account takeovers, now boasts enhanced features enabling unauthorized entry into additional platforms like Gmail and Outlook. Its expanded capabilities even extend to stealing crypto wallet balances and downloading further malicious payloads.
AI BUZZKILL DETECTS ROWDY PARTIES IN AN AIRBNB RENTAL
NodeStealer does not only hack your Facebook account but can spill over into other accounts, like Gmail and Outlook. (Credit: Bitdefender Labs)
MORE: THE DARK WORLD OF FACEBOOK ADS WHERE SCAMMERS ARE TRYING TO STEAL YOUR MONEY
How the attack unfolds
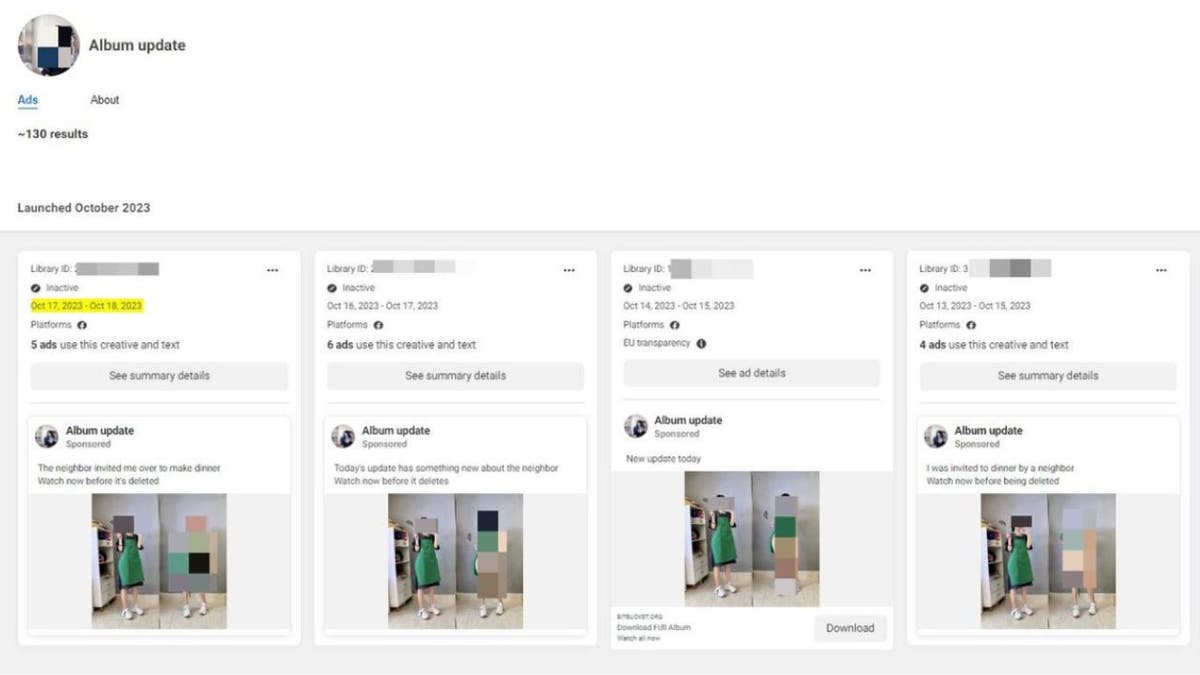
The attackers' modus operandi is both clever and calculated. Utilizing ad credit balances from hijacked business accounts, they run ads that distribute the NodeStealer malware to a specifically chosen group of people.
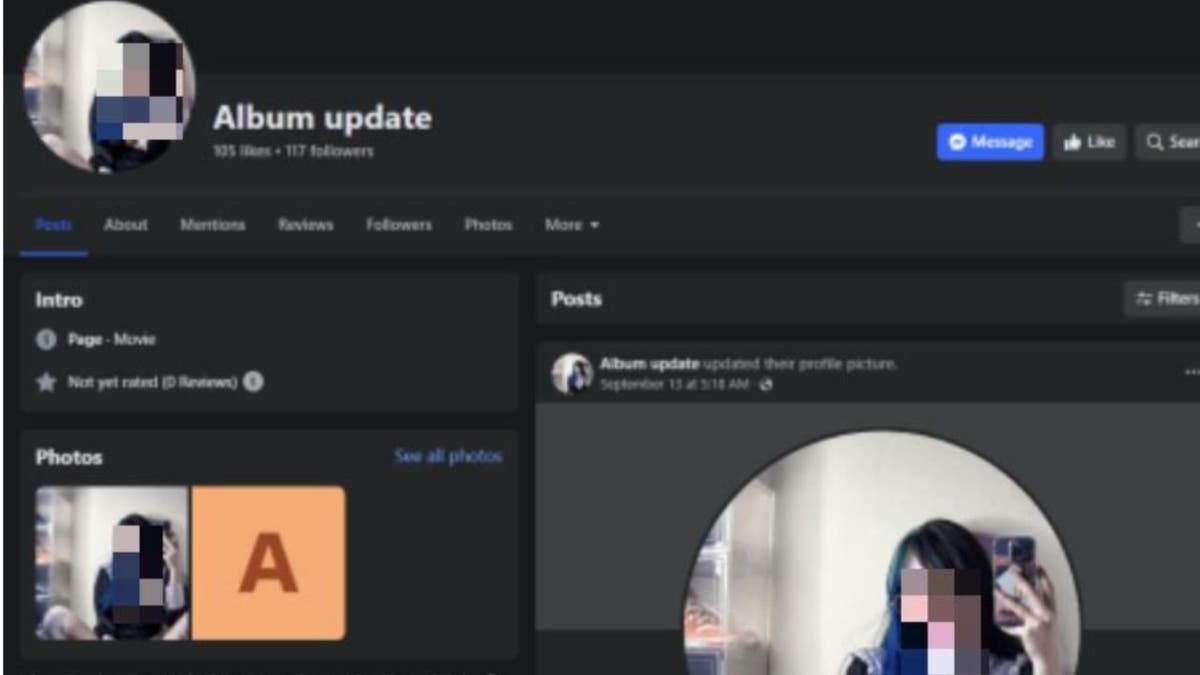
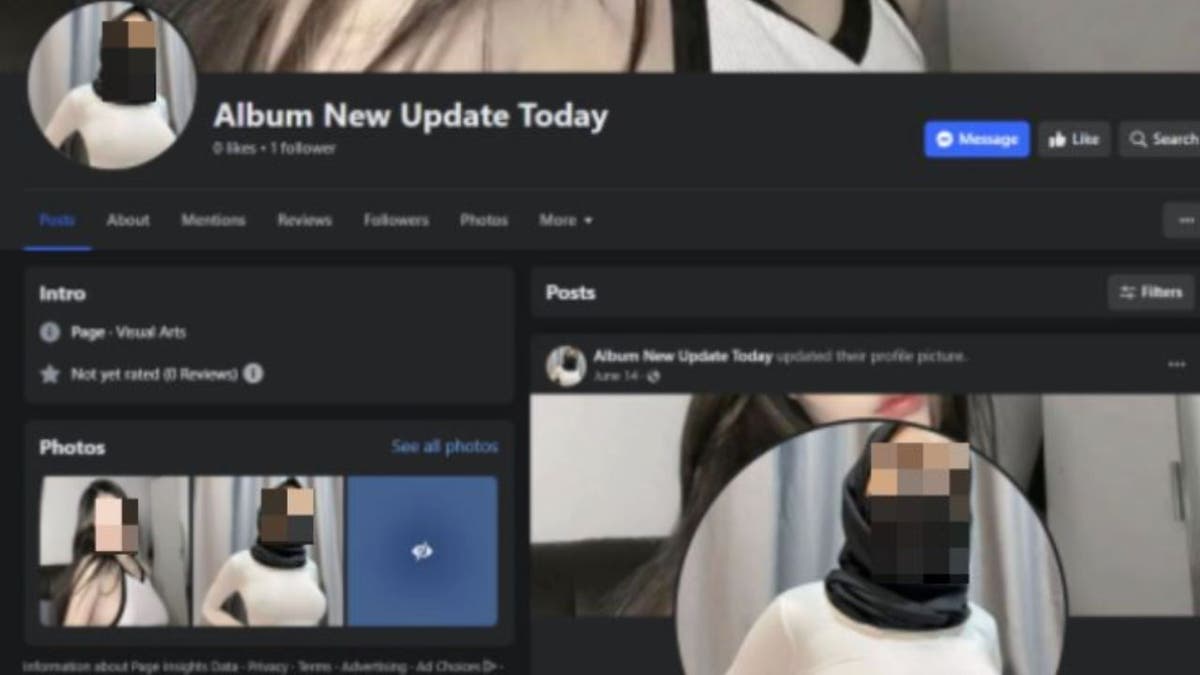
They establish Facebook pages with names like "Album Update" or "Hot Album Update Today," alluring users with the promise of exclusive, risqué content. Yet, the promised "albums" are merely a façade for spreading NodeStealer malware.
HOW TO ASSOCIATE A RINGTONE WITH ONE OF YOUR CONTACTS ON YOUR PHONE
Hackers use the allure of risqué content to entice Facebooks users to click on ads. (Credit: Bitdefender Labs)
MORE: TROUBLING MALWARE THREAT SPREADING ON FACEBOOK
Understanding what kind of damage this attack is capable of
When NodeStealer compromises your device, it doesn't just sit idly; it paves the way for cybercriminals to hijack your Facebook account and delve into your sensitive information. This breach can escalate quickly, with hackers potentially altering passwords and implementing additional security measures to lock you out of your own account.
The consequences can range from financial theft to identity fraud, with criminals using the stolen accounts to ensnare more victims, all while evading Meta's security measures.
HOW TO PROTECT YOUR APPLE IPHONE FROM CYBERATTACKS WITH LOCKDOWN MODE
Some of the consequences of this malware include financial theft and identity fraud. (Credit: Bitdefender Labs)
MORE: HOW SCAMMERS ARE SELLING COUNTERFEIT STAMPS ON FACEBOOK ADS
How to protect yourself from this persistent malware attack
To detect and defend against NodeStealer's nasty threat, you should adopt a multi-layered approach:
Implement robust security solutions from good antivirus protection: The cornerstone of digital defense is to have a reliable security solution installed on your device. Having good antivirus software actively running on your devices will alert you of any malware in your system, warn you against clicking on any malicious links in phishing emails, and ultimately protect you from being hacked. Review of the 2023 Best Antivirus Protection here.
Practice good cyber hygiene: Exercise caution in your digital interactions. Refrain from clicking on unsolicited links, particularly those associated with alarming notifications or ads urging you to download enticing media files.
Beware of suspicious ads: Specifically, for this NodeStealer campaign, you should be wary of any ad prompting the download of photo albums, especially if the source is Bitbucket, Gitlab, or Dropbox. Such ads are likely traps set by cybercriminals to deploy NodeStealer malware onto your device.
Scrutinize unusual account activity: Keep an eye out for any unusual activity on your accounts. Unexpected password-reset emails, unrecognized logins, or uninitiated security changes can be red flags signaling a compromised account.
Educate and inform: Share your knowledge about these threats with friends and family. The more informed people are, the less likely they are to fall victim to these schemes. Sign up for my security alerts by subscribing to my CyberGuy Newsletter here.
Kurt’s key takeaways
The evolution of NodeStealer attacks on Facebook is a stark reminder of the ongoing arms race between cybercriminals and security professionals. The proactive adoption of robust cybersecurity practices is our best defense in this digital age.
Remain alert to the ever-changing landscape of online threats, as illustrated by the provocative malvertising campaigns currently exploiting Facebook's vast network. You have to take proactive security on all of your connected technology seriously, as we’ve learned that we cannot rely on big tech or Uncle Sam to protect us from these growing threats.
How will the rise of sophisticated malware like NodeStealer change your approach to online security, and what steps do you plan to take to protect your digital identity on platforms like Facebook? Let us know by writing us at Cyberguy.com/Contact
For more of my tech tips and security alerts, subscribe to my free CyberGuy Report Newsletter by heading to Cyberguy.com/Newsletter
Ask Kurt a question or let us know what stories you'd like us to cover
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
Answers to the most asked CyberGuy questions:
● What is the best way to protect your Mac, Windows, iPhone and Android devices from getting hacked?
● What is the best way to stay private, secure and anonymous while browsing the web?
● How can I get rid of robocalls with apps and data removal services?
Copyright 2023 CyberGuy.com. All rights reserved.