CDC works to balance Americans' safety with the need for essential services
The CDC issues new guidelines on essential workers returning to the job after being exposed to COVID-19 after analyzing the latest data; Jonathan Serrie reports.
Get all the latest news on coronavirus and more delivered daily to your inbox. Sign up here.
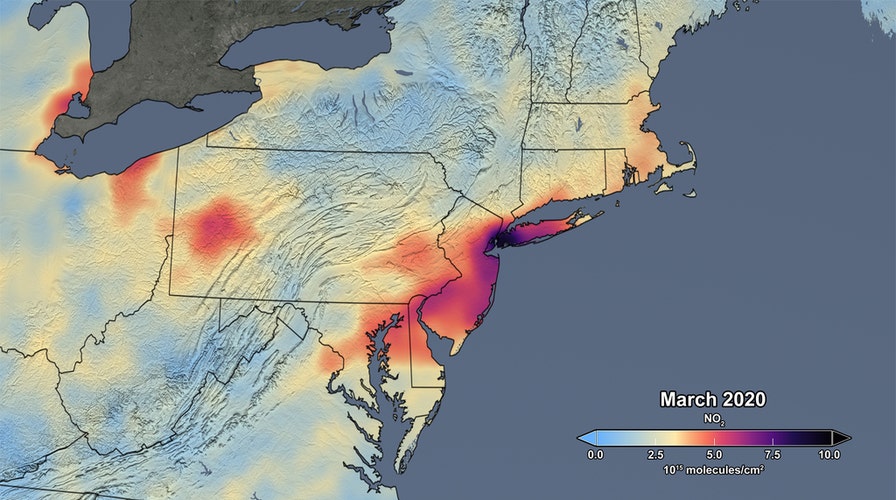
NASA satellite data has shown a 30 percent reduction in atmospheric nitrogen dioxide pollution in the northeastern U.S. during the coronavirus lockdown.
The average concentrations of atmospheric nitrogen dioxide were measured by the Ozone Monitoring Instrument on NASA’s Aura satellite during March and compared to the same period in prior years. Nitrogen dioxide, which is mainly emitted from burning fossil fuels and the generation of electricity, is a good indicator of human activity, according to the space agency.
New York State is the worst hit in the U.S. by the coronavirus outbreak, with at least 161,807 cases and 7,067 deaths as of Friday morning. New Jersey is the second worst-hit state, with 51,027 cases and 1,709 deaths as of Friday morning.
CHILLING VIDEO REVEALS HOW CORONAVIRUS SPREADS FROM A SINGLE COUGH IN A SUPERMARKET
“Though variations in weather from year to year cause variations in the monthly means for individual years, March 2020 shows the lowest monthly atmospheric nitrogen dioxide levels of any March during the OMI data record, which spans 2005 to the present,” explains NASA on its website. “In fact, the data indicate that the nitrogen dioxide levels in March 2020 are about 30% lower on average across the region of the I-95 corridor from Washington, DC to Boston than when compared to the March mean of 2015-19. Further analysis will be required to rigorously quantify the amount of the change in nitrogen dioxide levels associated with changes in emissions versus natural variations in weather.”
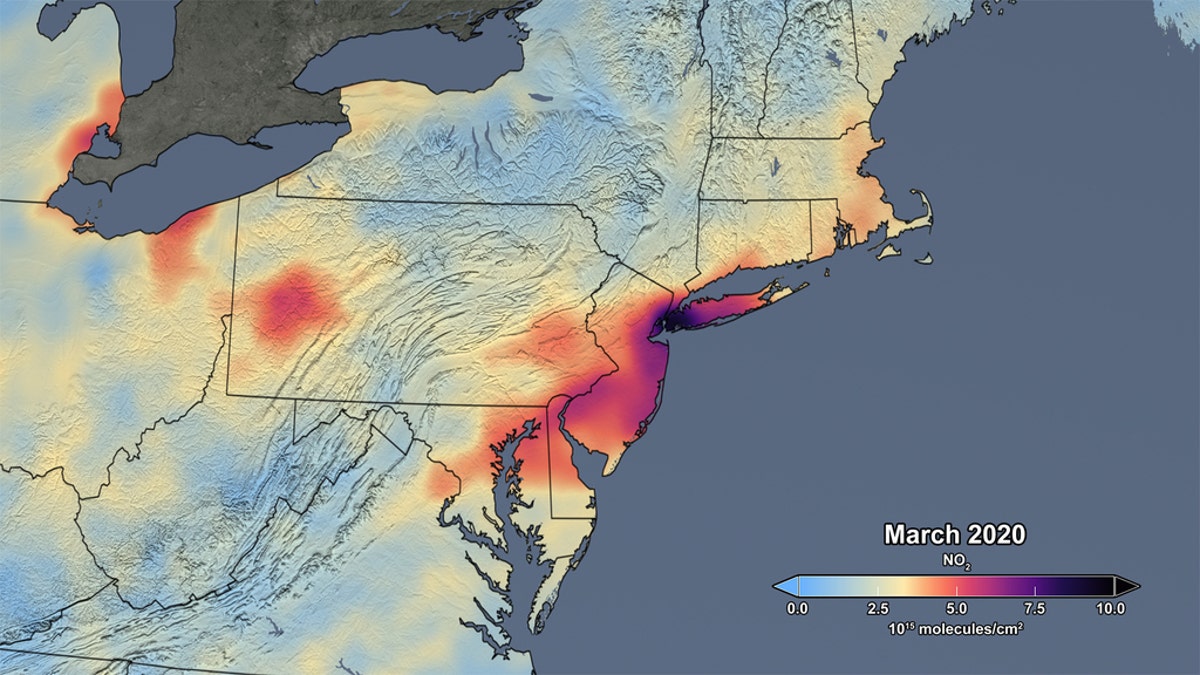
This image released by NASA shows the average concentration of atmospheric nitrogen dioxide measured in March of this year. (NASA/NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio)
NASA adds there are likely differences in nitrogen dioxide levels measured from space and measurements made at ground level. Satellites that measure nitrogen dioxide cannot see through clouds, the space agency explains, adding that its data shows pollution levels for days with low cloudiness.
With mass lockdowns in place across the globe, a number of studies have said that the coronavirus pandemic is having a major impact on pollution across the globe.
HOW CORONAVIRUS IS IMPACTING POLLUTION ACROSS THE GLOBE
“In California, the shutdown of businesses and activities related to #COVID19 has led to a decrease in nitrogen dioxide concentration,” NASA tweeted earlier this week.
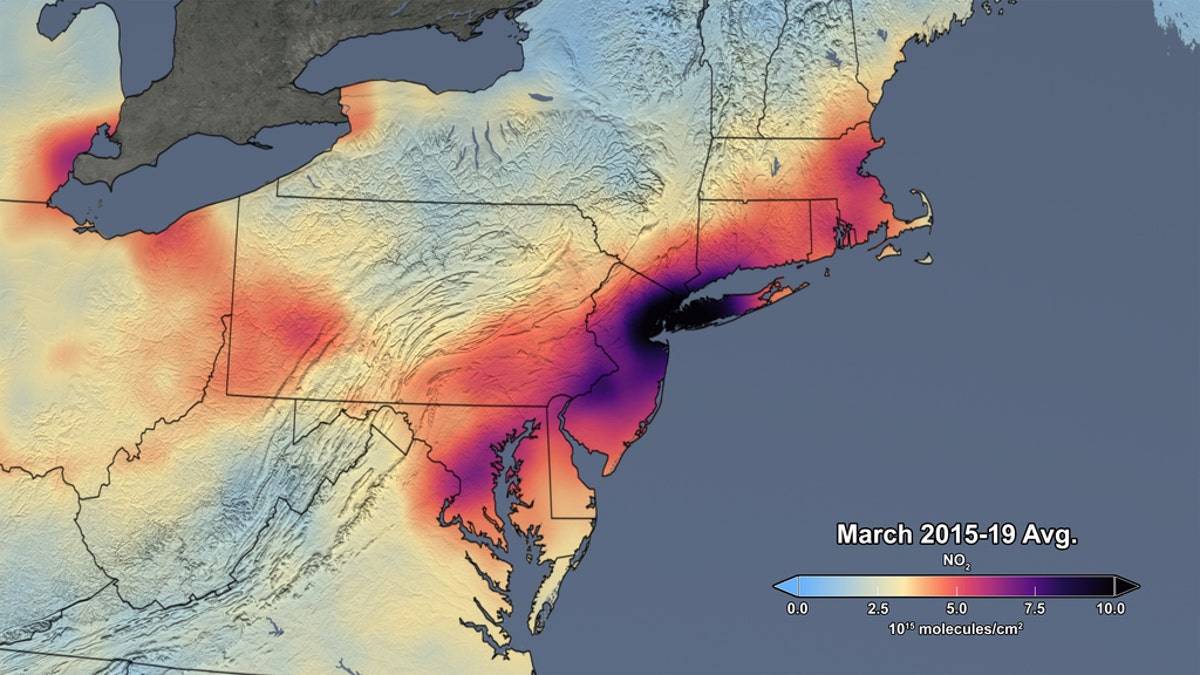
This image released by NASA shows the average concentration of atmospheric nitrogen dioxide in March of 2015-19. (NASA/NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio)
Researchers used data from the European Space Agency’s Sentinel-5P satellite to track the concentrations of nitrogen dioxide.
The European Space Agency also released satellite images that showed reductions in nitrogen oxide levels in several major cities across Europe.
CORONAVIRUS SOCIAL DISTANCING BUYING VALUABLE TIME FOR SCIENTISTS IN HUNT FOR CURE: BIOCHEMIST
In the U.K., a recent report by solar power specialists The Eco Experts estimates that the country’s CO2e (carbon dioxide equivalent) emissions are set to drop by 28.22 million tonnes over the 12-week period following the implementation of social distancing measures on March 19.
CLICK HERE FOR COMPLETE CORONAVIRUS COVERAGE
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
As of Friday morning, at least 1.6 million coronavirus cases have been diagnosed worldwide, at least 466,299 of which are in the U.S. The disease has accounted for at least 96,787 deaths around the world, including at least 16,686 people in the U.S.
Follow James Rogers on Twitter @jamesjrogers