(MandicJovan)
CHICAGO – The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has ordered blood banks in Florida's two most densely populated counties to stop collecting blood as health officials determine whether Zika has begun transmission in the continental United States.
Florida has been investigating four possible cases of local transmission in Miami-Dade County and Broward County. It is the first U.S. state to report cases that may not be related to travel to other countries with active outbreaks.
Zika has struck hardest in Brazil, where the outbreak was first detected last year, and has since spread rapidly through the Americas. The virus can cause a rare birth defect, microcephaly, in newborns whose mothers have been infected, and is believed to be linked to Guillain-Barre syndrome in adults.
Zika most commonly infects people via mosquito bite. But reports of the virus being transmitted through sex and blood transfusions has prompted public health officials to recommend additional precautions for sexual partners and blood banks.
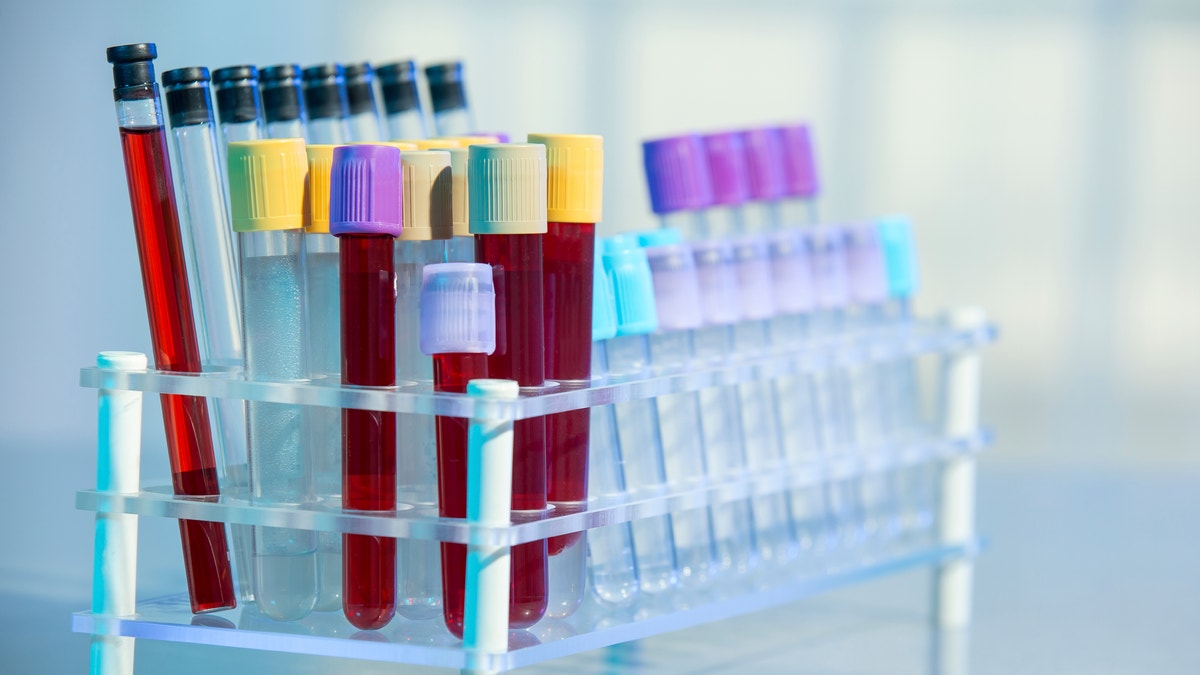
In a statement posted online on Wednesday, the FDA said blood centers in the two Florida counties should stop collecting blood until they can test each unit or put in place technology that can kill pathogens in the blood.
The FDA also recommended that nearby counties implement the same measures as it moves to prevent transmission of the virus through the blood supply.
OneBlood, Florida's biggest blood collection center, said it will begin testing all of its collections for Zika virus, effective July 29, using an investigational screening test and that it is working as quickly as possible to comply with the FDA's request.
The FDA has authorized the emergency use of several investigational Zika screening tests, including products made by Hologic Inc and Roche Holding AG.
The agency has also approved a pathogen inactivation technology made by Cerus Corp that kills the virus in blood platelets and plasma. The company is conducting clinical trials to show it can also kill pathogens in red blood cells.
The United States uses roughly 12 million units of red cells, four million plasma units and two million units of platelets a year.
Unlike oxygen-carrying red blood cells, which can be kept for 42 days in a refrigerator, or plasma, which keeps for a year if frozen, platelets have a shelf life of just four to seven days.
Platelets in general tend to be scarce because there are fewer donors. It can take up to two hours to extract platelets using an apheresis machine, said Dr. Richard Benjamin, chief medical officer for Cerus. And because of their short shelf life hospitals typically do not keep much surplus.
It can be hard to source them from elsewhere, too. By the time they are flown from one place to another they may only have two days of life left.
"All we need is a few more Zika hotspots and there will be a shortage of platelets across the country," Benjamin said.
The FDA's action follows Florida's announcement on Wednesday that it had identified two additional Zika cases - one more in each county - that were not related to travel to an area where the virus is being transmitted.
A CDC spokesman said on Wednesday that "evidence is mounting to suggest local transmission via mosquitoes" in South Florida, noting that the cases fit transmission patterns seen with prior mosquito-borne outbreaks such as Chikungunya.
FDA said it will continue to monitor the situation in Florida in cooperation with the CDC and state public health authorities and provide updates as additional information becomes available.