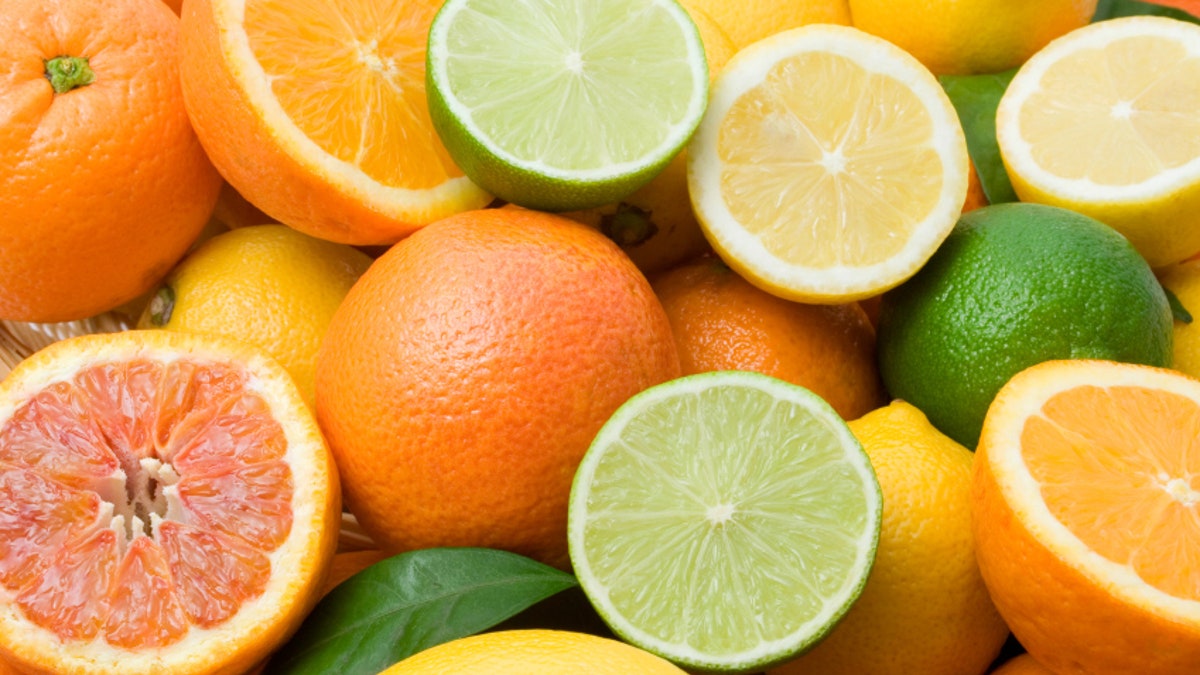
Lemon, lime, tangerine, orange and grapefruit background
Most people know a thing or two about vitamin C, like that it’s in orange juice, or that without it you can develop scurvy (as sailors famously did). But myths about this essential nutrient are also still fairly common, and the truth is our knowledge about its benefits and functions continues to evolve.
For example, did you know that vitamin C might help your cardiovascular health? A brand new study from University of Colorado, Boulder, found that that a 500 mg time-released dose of vitamin C had a protective effect on blood vessels that was similar to a walking workout, prompting some to dub vitamin C the “exercise pill.” Now, I wouldn’t go that far—the study was small, including just 35 inactive overweight or obese adults. And the reasons to exercise go beyond blood vessel health. But this certainly suggests that vitamin C does far more for our bodies than support immunity.
What else don’t you know about vitamin C? Test your nutrition IQ with my 5 myths and facts about this fascinating nutrient.
RELATED: 12 Foods With More Vitamin C Than Oranges
Blasting a cold with vitamin C will fight it off: myth
Now that cold and flu season is officially ramping up, a lot of people are loading up on OJ and C supplements to avoid getting sick. But sadly, that may not be as beneficial as you think.
While some research shows that people who regularly take vitamin C supplements may have slightly shorter colds or somewhat milder symptoms, for most people, boosting vitamin C doesn’t reduce the risk of catching the common cold. I say “most people” because there are studies that show that vitamin C cut cold risk by 50 percent in male athletes, but not in females.
It is true that vitamin C is critical for immune function, and that it plays a key role in wound healing. But the best way to keep your immune system strong is to eat healthfully, including vitamin C rich produce, all the time. Unfortunately, the latest stats show that three-quarters of Americans fall short of the recommended minimum two daily cups of fruit and 87 percent fail to eat the advised three daily cups of veggies. Fill that gap and you’ll easily take in at least 200 mg of vitamin C daily, enough to keep your immune system well supported every day so you won’t need to play catch up.
RELATED: 26 Quick, Healthy Juice and Smoothie Recipes
Vitamin C deficiencies are rare: fact
Our bodies cannot produce vitamin C, which is what makes this nutrient essential, meaning we must obtain it from food. But these days a deficiency serious enough to cause symptoms, which can include bleeding gums and nosebleeds, swollen joints, rough, dry skin, and bruising, is pretty rare.
The recommended daily target for adults is 75 mg for women, and 90 for men, although many experts believe it should be raised to 200 mg, the amount that saturates the body’s tissues. One medium orange provides about 70 mg, and scurvy can be prevented with as little as 10 daily mg of vitamin C. In other words, you’re probably not at risk of a true deficiency—but that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t strive to get enough.
Citrus is the best source of vitamin C: myth
While citrus is an excellent source of vitamin C, a veggie—bell peppers—comes out on top. One cup of chopped raw red bell pepper (about the size of a tennis ball) packs 200-300 mg of vitamin C, about 100 more than a cup of OJ. Other good sources include broccoli, Brussels sprouts, kiwi, strawberries, papaya, pineapple, and cantaloupe, as well as (of course) citrus fruits, like oranges, tangerines, and grapefruit.
RELATED: Superfoods that Fight Colds
Adequate vitamin C intake helps weight loss: fact (mostly)
A low blood level of vitamin C has been linked to having a higher BMI, body fat percentage, and waist circumference, compared to people with normal levels. And a study from Arizona State University found that vitamin C status might affect the body’s ability to use fat as a fuel source—during both exercise and at rest.
To reap vitamin C’s weight control benefits your best bet is to focus on being active, and making your meals with colorful produce that’s naturally rich in vitamin C.
RELATED: Eat Your Way to Health and Happiness
You can’t get too much vitamin C: myth
Your body can’t store vitamin C, so when you consume more than you need the surplus is eliminated by your kidneys in urine. That doesn’t mean however that big doses can’t create unwanted side effects. Vitamin C is one of the nutrients that has an established Tolerable Upper Intake Level, or UL, essentially the maximum advised intake, from both food and supplements combined. For vitamin C it’s 2,000 mg a day, and while some people may be fine taking in this amount or more, megadoses of vitamin C supplements have been shown to trigger bloating and digestive upset, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, headaches, insomnia, and kidney stones. Bottom line: more definitely isn’t better; just enough is in fact just right!
Cynthia Sass, MPH, RD, is Health's contributing nutrition editor. She privately counsels clients in New York, Los Angeles, and long distance. Cynthia is also the sports nutrition consultant to the New York Rangers NHL team and the New York Yankees MLB team, and is board certified as a specialist in sports dietetics.